Establishing an athletic hall of fame requires more than enthusiasm—it demands clear, defensible criteria that ensure fairness, maintain program credibility, and stand the test of time. Athletic directors and recognition committees face a fundamental challenge: how do you objectively measure greatness across different sports, eras, and achievement types while building consensus among stakeholders with competing perspectives?
Effective hall of fame criteria balance objective achievement measurements with contextual considerations, creating transparent selection frameworks that the entire community can understand and support. This guide provides the templates, evaluation matrices, and documentation standards that transform subjective debates into structured decision-making processes.
Establishing Your Foundation: Core Criteria Categories
Athletic hall of fame criteria typically organize into distinct categories, each requiring specific measurement standards and documentation requirements.
Individual Achievement Standards
The most straightforward hall of fame category recognizes individual athletic excellence through measurable accomplishments.
State-Level Recognition
Athletes who receive state-level honors demonstrate achievement beyond local or conference competition. Common standards include:
- All-state first team selections in any sport
- State championship individual titles (track events, wrestling weight classes, swimming events)
- State tournament MVP or player of the year recognition
- State record holders in officially tracked statistics
State-level criteria provide objective verification—either an athlete received the recognition or didn’t—minimizing subjective evaluation and potential controversy.
School Record Holders
Athletes who set school records demonstrate measurable superiority over program history. When establishing record-holder criteria:
Define qualifying records: Not all statistical categories merit hall of fame consideration. Focus on primary statistics—points scored, yards gained, wins recorded—rather than obscure secondary metrics.
Establish longevity requirements: Should records need to stand for a minimum period before triggering hall of fame eligibility? Many programs require records to stand at least 5-10 years, ensuring they represent sustained excellence rather than statistical anomalies.
Account for era differences: A 1970s basketball scoring record achieved before the three-point line differs contextually from modern records. Document how you’ll address competitive era changes when evaluating historical records.
Address tie scenarios: What happens when multiple athletes share a record? Define whether tied record holders all receive recognition or if tie-breaking criteria apply.

Team Championship Standards
Championship teams represent collective achievement requiring different evaluation approaches than individual honors.
State Championships
State championship teams typically qualify automatically for hall of fame recognition. However, specification details matter:
Classification levels: Do all state championship teams receive recognition regardless of competitive classification? A Class A state champion competes in a different context than a Class AAAA champion. Document whether you recognize championships across all classifications equally or create tiered recognition.
Tournament placement: Do state runner-up teams qualify for recognition? What about semifinalists? Establishing clear placement thresholds prevents expansion debates as marginal teams seek inclusion.
Team vs. individual recognition: When a championship team enters the hall of fame, does every team member receive individual recognition, or does the team receive collective acknowledgment? Define whether you’ll display full rosters with individual profiles or team-level entries with group photographs.
Conference Championships
Conference championships represent significant achievement but occur more frequently than state titles. Many programs establish additional qualifying criteria:
- Undefeated conference records
- Conference championships combined with deep playoff runs
- Multiple consecutive conference titles
- Conference championships in historically dominant competitive conferences
Historic Season Milestones
Some teams achieve remarkable records without winning championships. Consider recognition standards for:
- Undefeated regular seasons
- School-record win totals
- Historically dominant statistical achievements (lowest points allowed, highest scoring average)
- Significant advancement beyond typical program expectations
These milestone criteria require careful definition. What constitutes “significant advancement” varies by program tradition—a semifinal appearance might be routine for perennial powers but historic for emerging programs.
Multi-Sport Athlete Recognition
Athletes competing successfully in multiple sports demonstrate exceptional versatility and year-round athletic commitment.
Minimum achievement standards: Define minimum achievement levels required across multiple sports. Common frameworks include:
- Varsity letters earned in 3+ sports during a single year
- All-conference recognition in 2+ sports
- Varsity participation across all three athletic seasons
- State-level recognition in multiple sports
Evaluation weighting: Should multi-sport participation alone merit hall of fame consideration, or must multi-sport athletes also meet single-sport achievement standards? Document whether multi-sport versatility represents a standalone criterion or an enhancement to primary achievement evaluation.

Nomination and Selection Process Framework
Clear, documented processes ensure transparent, consistent selection that maintains community trust and program credibility.
Nomination Procedures
Eligibility timeline: Establish when athletes become eligible for nomination. Common approaches include:
- Minimum years since graduation (typically 5-10 years)
- Minimum years since final athletic participation
- Immediate eligibility for truly exceptional achievement (Olympic medals, professional careers)
- Rolling eligibility where nominees can be considered in subsequent years if not selected initially
The timeline prevents selection based on recent memory rather than sustained historical significance while acknowledging rare achievements that merit immediate recognition.
Who can nominate: Define who may submit nominations:
- Any community member through public nomination forms
- Restricted nomination by coaches, athletic directors, or committee members only
- Combination approach where public can suggest candidates that committee members formally nominate
Open nomination processes increase community engagement but generate higher volumes requiring more committee time for initial screening. Restricted approaches reduce administrative burden but may miss deserving candidates without strong advocates.
Required documentation: Specify what information nominators must provide:
- Athlete biographical details (name, graduating class, sports participated in)
- Specific achievements and recognition received
- Statistical records and verification sources
- Supporting materials (photos, newspaper clippings, awards documentation)
- Letters of recommendation from coaches, teammates, or community members
Detailed documentation requirements ensure committees have sufficient information for informed evaluation while discouraging frivolous nominations lacking substantive achievement basis.
Selection Committee Structure
Committee composition: Effective committees balance diverse perspectives while maintaining manageable size:
- Athletic director (typically serves as chair)
- Current and former coaches representing different sports
- School administration representative
- Booster club or alumni association representation
- Community member or local media representative
Aim for 5-9 members—enough for diverse perspective but small enough for efficient deliberation. Larger committees struggle to reach consensus and coordinate scheduling.
Term limits and rotation: Implement term limits preventing permanent committee control by any individuals:
- 3-year terms with maximum consecutive term limits
- Staggered rotation ensuring continuity (don’t replace entire committee simultaneously)
- Required breaks between terms for members who reach term limits
Rotation brings fresh perspectives while preventing institutional knowledge loss if all experienced members depart simultaneously.
Recusal protocols: Document when committee members must recuse themselves from deliberations:
- Close family members under consideration
- Former athletes they personally coached
- Situations where financial interests or personal conflicts exist
Clear recusal standards prevent appearance of favoritism that undermines program credibility.

Evaluation Matrix and Scoring Framework
Transform subjective judgment into structured evaluation by implementing scoring frameworks that quantify achievement relative to established criteria.
Weighted criteria categories: Assign point values to different achievement types:
| Achievement Category | Point Value |
|---|---|
| State championship participation | 10 points |
| All-state first team selection | 15 points |
| School record holder | 12 points |
| Conference championship participation | 5 points |
| All-conference first team | 6 points |
| Multi-sport letter winner (3+ sports) | 8 points |
| Post-high school athletic continuation (college scholarship) | 7 points |
| Professional athletic career | 20 points |
| Olympic or international competition | 25 points |
Adjust point values reflecting your program’s priorities and competitive context. Programs with strong conference competition might weight conference achievements higher than those in less competitive conferences.
Threshold requirements: Establish minimum point totals for automatic consideration and higher thresholds for guaranteed induction:
- 30+ points: Strong candidate deserving serious consideration
- 50+ points: Presumptive inductee unless extenuating circumstances exist
- 75+ points: Automatic induction without requiring committee vote
Thresholds provide objectivity reducing personal bias while allowing committee discretion for borderline cases or contextual factors not captured by point systems.
Contextual adjustment factors: Scoring systems capture quantifiable achievements but miss context. Document how committees should consider:
- Era adjustments: Three-sport athletes were more common before year-round sport specialization
- Program maturity: Early program achievements occurred against weaker competition
- Competitive classification changes: Schools that moved between competitive classifications
- Injury impact: Athletes whose careers were shortened by injury despite clear trajectory toward greater achievement
- Character and sportsmanship: How character factors influence selection when achievement levels are comparable
Contextual factors shouldn’t override objective achievement but provide frameworks for committee deliberation when candidates cluster around threshold points.
Documentation Standards and Record-Keeping
Sustainable hall of fame programs maintain comprehensive documentation supporting each selection and creating historical records for future reference.
Achievement Verification Requirements
Before finalizing inductions, verify claimed achievements through reliable sources:
Official recognition verification: Confirm all-state selections, championship participation, and official awards through:
- State athletic association records and archives
- Conference office documentation
- School yearbooks and athletic program records
- Newspaper archives from achievement periods
- Team records and coaching documentation
Don’t rely solely on memory or hearsay. When historical documentation proves difficult to locate, note verification limitations in permanent records.
Statistical record confirmation: For athletes recognized based on school records:
- Document official record books showing the athlete held the record
- Verify dates the record was set and (if applicable) when it was broken
- Photograph record boards or publish documented record lists
- Cross-reference multiple sources when possible to confirm accuracy
Statistical discrepancies occasionally surface when informal records differ from official documentation. Establish source hierarchy determining which records receive precedence when conflicts arise.
Inductee Profile Standards
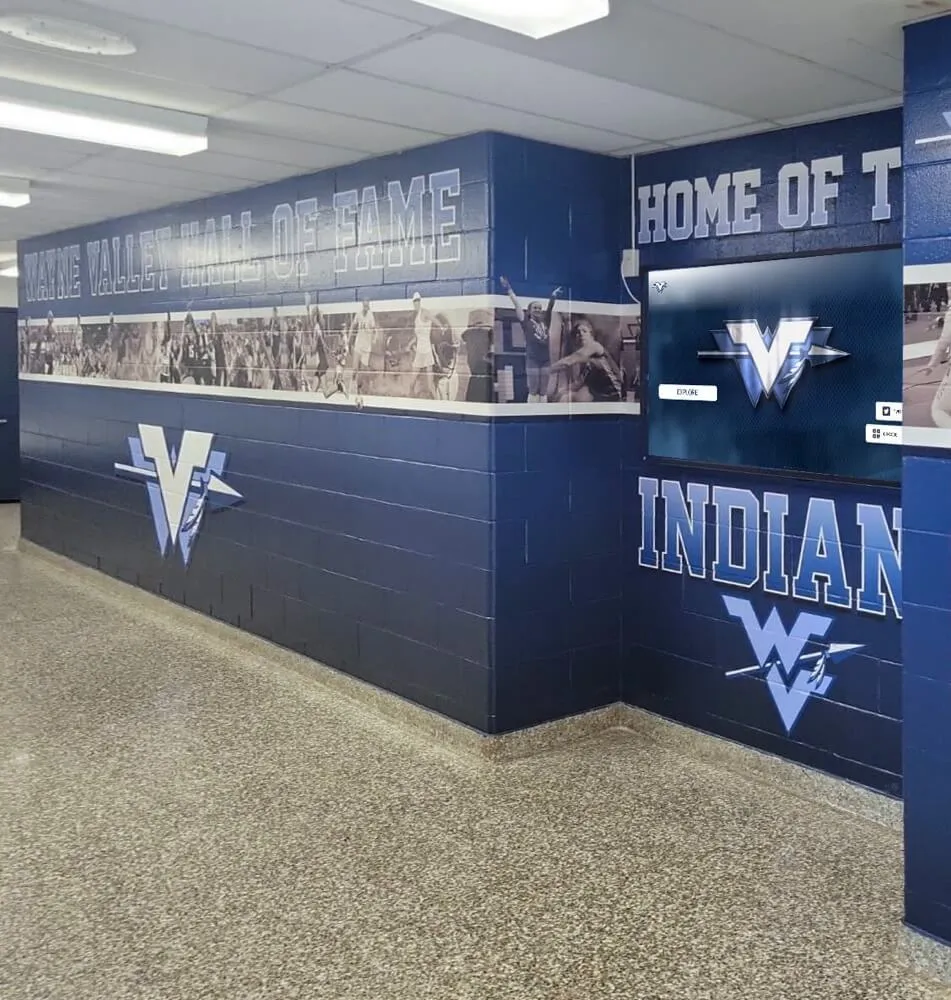
Create consistent biographical profiles for each inductee ensuring comprehensive, professional documentation. For traditional physical displays, this might require balancing detail with space limitations, but modern digital hall of fame solutions enable rich multimedia profiles impossible with static plaques.
Required profile elements:
- Full name (as it appears in official school records)
- Graduating class year
- Sport(s) participated in and positions played
- Varsity letters earned and years of participation
- Championships and tournament achievements
- Individual recognition (all-state, all-conference, player of the year)
- School records held (with statistical documentation)
- Post-high school athletic continuation (college, professional, international)
- Induction year and class
Enhanced profile elements for digital systems:
- Multiple photographs spanning athletic career
- Video highlights from competitions and championship moments
- Statistical tables showing career performance
- Coach testimonials and scouting reports
- Teammate reflections and memorable game stories
- Career timelines showing progression and milestone moments
- Post-athletic career updates and current biographical information
When implementing comprehensive athletic recognition programs, digital platforms allow unlimited content updates ensuring profiles remain current as inductees achieve new milestones in their post-athletic lives.
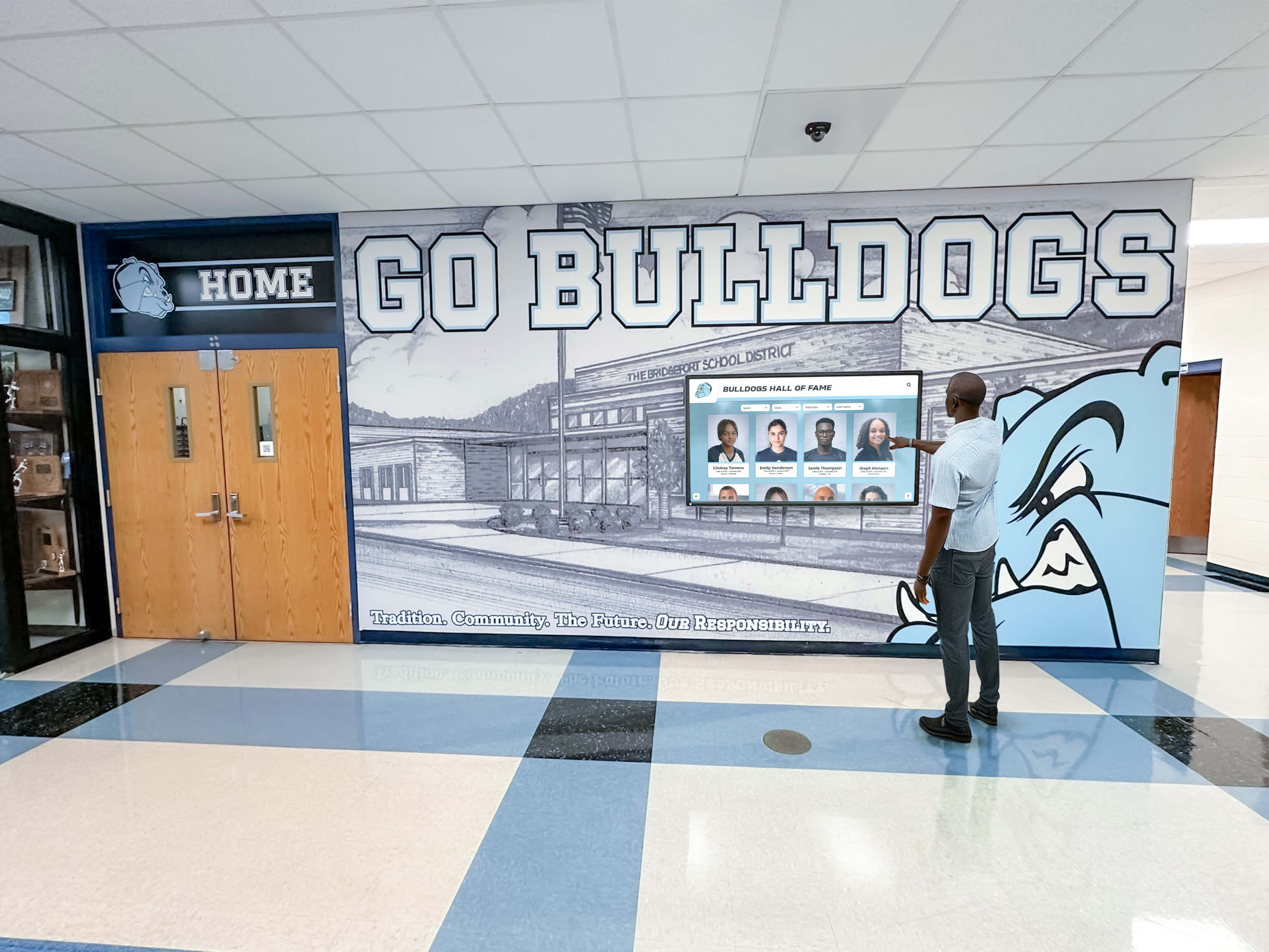

Special Consideration Categories
Beyond standard athlete recognition, many programs create special categories addressing unique circumstances or honoring non-athlete contributors.
Coaches and Contributors
Athletic directors often ask whether coaches should be included in halls of fame focused primarily on athlete achievement. Creating separate criteria for coaching excellence maintains distinction between player and coach recognition while honoring those who shaped program success.
Coaching achievement criteria:
- Minimum years coaching at the institution (typically 10+ years)
- Championship teams coached (conference, district, regional, state)
- Career win totals or winning percentage thresholds
- Development of all-state, all-conference, or college scholarship athletes
- Conference or state coach of the year recognition
- Program building or significant competitive advancement
- Contribution to sport beyond local program (clinics, state association leadership)
Contributor recognition: Some programs honor administrators, boosters, officials, or community members who made extraordinary contributions:
- Long-term athletic director service through significant program growth
- Major facility funding or booster club leadership
- Team physicians, athletic trainers, or medical contributors
- Officials who served program for decades
- Media members who chronicled and promoted athletic achievement
Contributor categories require careful definition preventing expansion that dilutes athlete recognition focus. Many programs limit contributor inductions to one per induction class or require exceptional contribution standards.
Pioneer and Trailblazer Recognition
Athletes who faced unique challenges or achieved “firsts” merit consideration even when their competitive achievements don’t reach standard criteria levels:
- First athletes in newly established sports programs
- Athletes who competed during eras with limited opportunities (early women’s athletics)
- Athletes who broke barriers or achieved firsts for underrepresented groups
- Athletes who maintained excellence despite extraordinary personal circumstances
Pioneer criteria acknowledge that contextual significance sometimes matters as much as competitive statistics. However, define pioneer standards carefully to prevent creating separate, lower standards that inadvertently imply reduced expectations.
Posthumous Inductions
Tragically, some athletes die before becoming eligible for hall of fame consideration. Establish clear standards for posthumous recognition:
Standard posthumous induction: Athletes who die after meeting normal eligibility timelines can be considered and inducted using standard criteria. No special considerations apply beyond timing sensitivity and family notification.
Early posthumous consideration: Athletes who die before normal eligibility timelines may receive expedited consideration if:
- They clearly met achievement standards despite shortened timelines
- Competitive trajectory clearly indicated future qualification
- Athletic career was complete (graduated or aged out) even if death occurred before minimum waiting period
Memorial recognition vs. hall of fame induction: Some programs distinguish between memorial recognition honoring athletes who died young and formal hall of fame induction based on achievement criteria. Memorial recognition focuses on person and legacy while hall of fame induction requires meeting achievement standards.
Address Common Selection Challenges
Even with clear criteria, committees face recurring challenges requiring policy guidance and precedent-setting decisions.
Comparing Across Different Sports
How do you compare a state champion wrestler with a three-sport athlete who lettered in football, basketball, and track but never won championships? Evaluation frameworks must account for sports-specific contexts.
Sport-specific achievement standards: Recognize that achievement difficulty varies by sport context:
- Team sport championships: Require collective success impossible for individual athletes to control
- Individual sport state titles: Represent personal achievement within competitive field
- Participation numbers: Sports with high participation face more competitive state qualification
Consider sport-specific paths to qualification rather than universal standards that inadvertently favor certain sports. A scoring framework might award:
- State championships: 15 points (regardless of sport)
- Individual state titles: 18 points (reflecting personal achievement)
- Team championships where athlete played critical role: Additional consideration based on statistical contribution
The goal is creating frameworks where excellence in any sport can achieve hall of fame recognition without disadvantaging athletes in team sports or less prominent programs.
Balancing Historical and Recent Achievement
Long-established programs face challenges balancing recognition of historical pioneers with contemporary athletes competing under different conditions.
Era representation policies: Some programs implement policies ensuring historical era representation:
- Minimum inductee percentages from different decades
- Special historical recognition classes periodically celebrating early program achievements
- Rotating committee focus between recent candidates and historical research
These approaches prevent hall of fame programs from becoming exclusively focused on recent, well-remembered athletes while earlier pioneers are forgotten.
Achieving competitive era adjustments: Athletic competition evolves. Today’s athletes benefit from year-round training, specialized coaching, and nutrition science unavailable to earlier generations. Conversely, historical athletes faced fewer competitive opportunities—limited playoffs, shorter seasons, less media coverage.
Document how committees should weigh era differences when evaluating comparable achievement levels from different periods. Generally, evaluate athletes against their competitive era rather than applying modern standards to historical achievement or discounting current accomplishment because modern advantages exist.
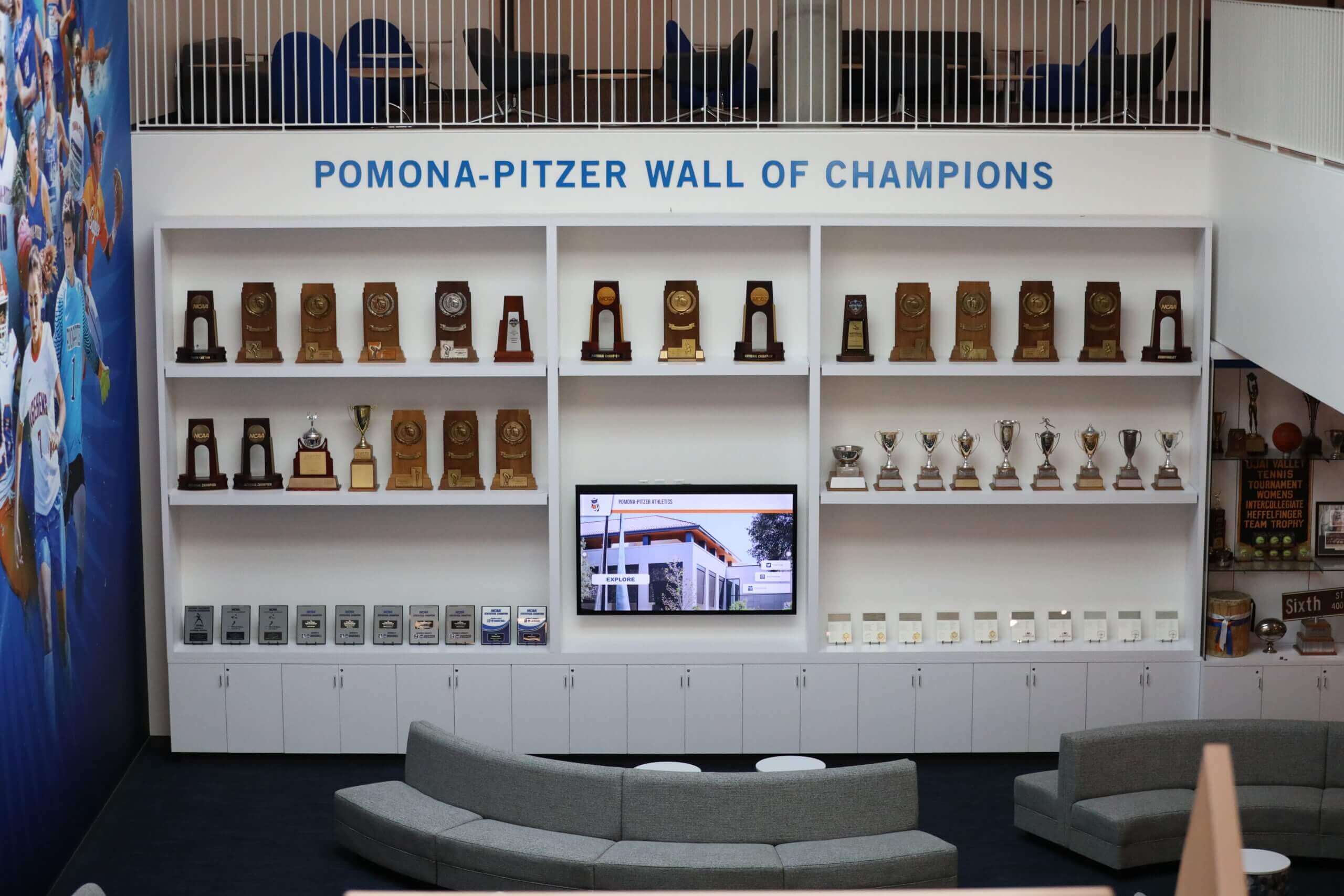

Managing Family and Community Pressure
High-profile nominations generate community interest and family advocacy that can pressure committees toward inclusion despite marginal achievement alignment with documented standards.
Maintain selection confidentiality: Committee deliberations should remain confidential. Public discussion of specific candidate weaknesses creates community friction and discourages future participation.
Document decisions thoroughly: When committees choose not to induct nominated candidates, document specific criteria gaps in internal records. If future questions arise, documented rationales prevent having to rely on memory or reconstruct reasoning.
Communicate standards publicly: Make selection criteria publicly available so nominators understand expectations before submitting nominations. Clear public standards help manage expectations and provide objective reference points when discussing selection outcomes.
Annual nomination allowance: If strong candidates aren’t selected in their first eligible year, allow renomination in subsequent years. Sometimes timing matters—competitive nomination pools or missing documentation might prevent initial selection even for deserving candidates.
Annual Induction Class Size and Timing
Programs must decide how many inductees to recognize annually and when inductions occur.
Determining Optimal Class Sizes
Fixed annual numbers: Some programs induct fixed numbers each year (e.g., five inductees annually). Fixed numbers create predictability and ensure regular recognition momentum. However, rigid numbers may force inclusion of marginal candidates during weak nomination years or exclude deserving candidates during strong nomination years.
Flexible ranges: Other programs establish ranges (e.g., 3-7 inductees annually). Flexibility allows committees to respond to nomination quality—smaller classes during weak years, larger classes during strong years—while maintaining some structure preventing excessive growth or complete inactivity.
Achievement-based selection: Rather than predetermined numbers, some committees induct all candidates meeting threshold criteria. This approach ensures recognition is based purely on achievement merit rather than artificial quotas. However, it can create unpredictable recognition timing and potential years with no inductees or unexpectedly large classes.
Most programs find flexible ranges provide the best balance—enough structure to maintain regular recognition while allowing response to nomination quality variations.
Induction Ceremony Timing
Homecoming ceremonies: Many schools conduct inductions during homecoming weekends, leveraging high community attendance, alumni presence, and celebratory atmosphere. Homecoming timing provides natural audience and commemorative context.
Annual banquets: Dedicated recognition banquets separate from other events allow focused celebration and extended program time for multiple inductees. Ticketed events can fund program operations while creating formal occasion worthy of hall of fame honor.
Athletic season alignments: Some programs time inductions to align with dominant sports—football programs during football season, basketball programs during basketball season. This approach maximizes relevant audience attendance but may inadequately recognize athletes from other sports.
Annual consistency: Regardless of specific timing, maintain consistent annual schedules. Irregular, sporadic inductions undermine program prestige and community anticipation.
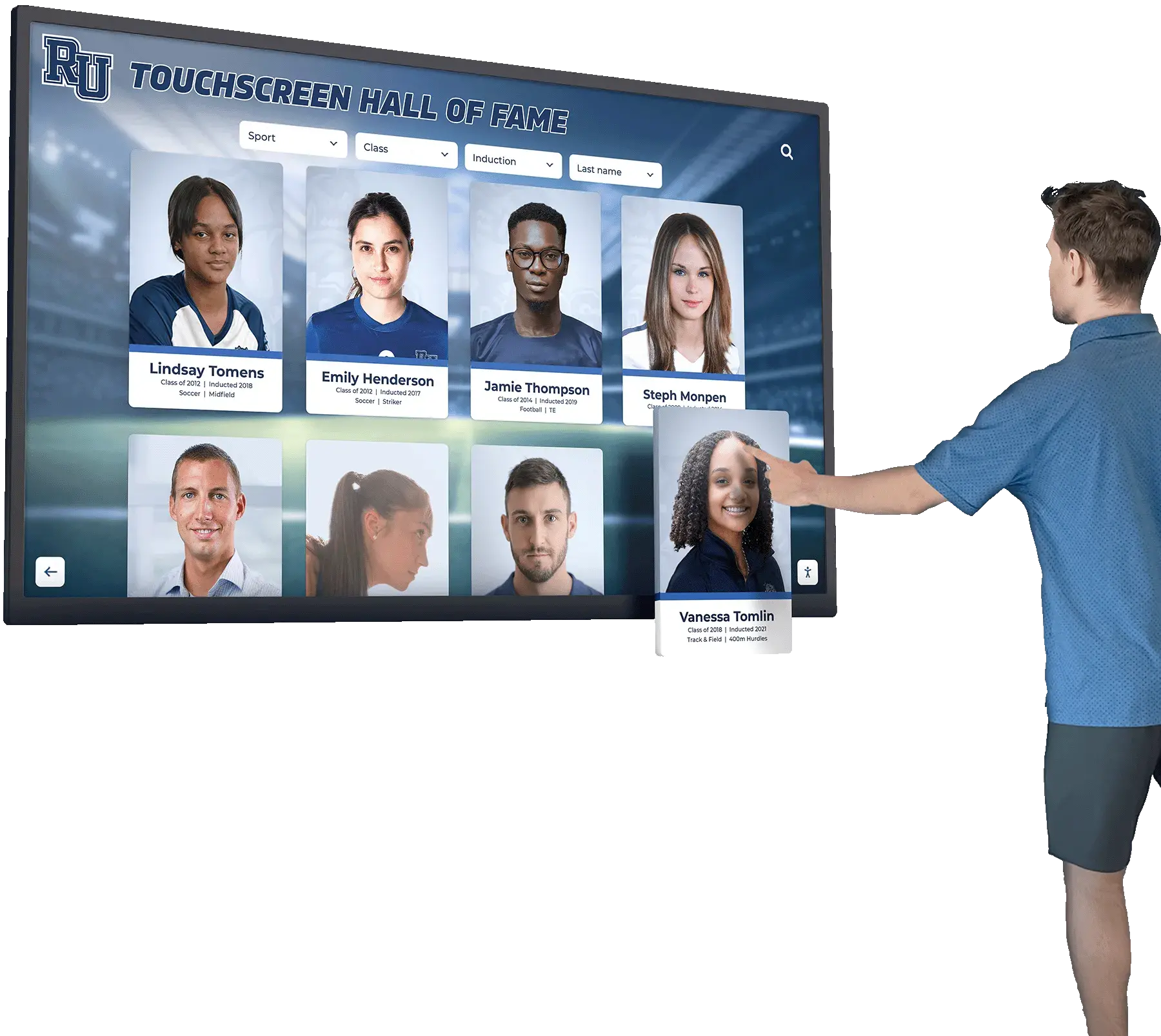
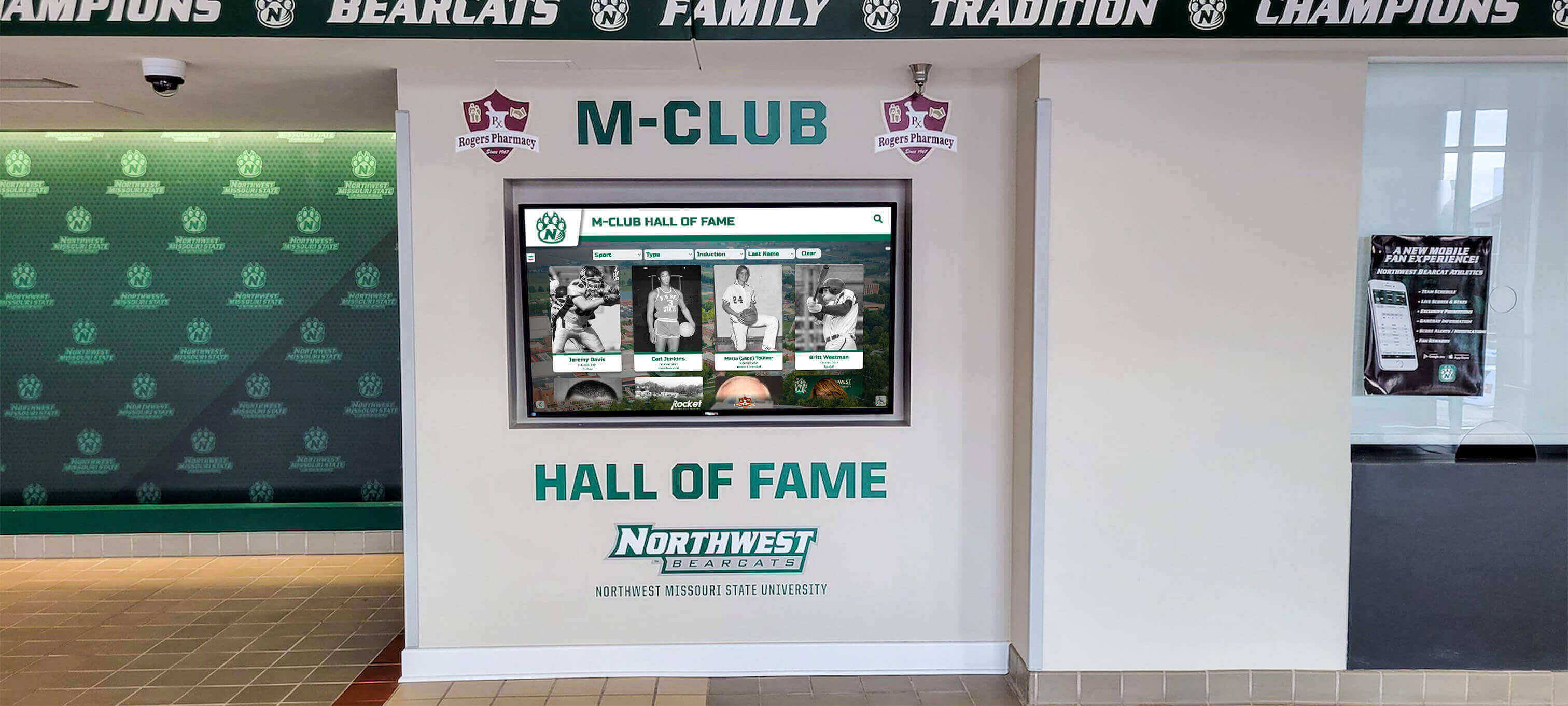
Many schools implementing digital recognition displays find that platforms like Rocket Alumni Solutions integrate seamlessly with annual induction ceremonies—new inductee profiles can be added remotely before ceremonies, revealed during induction presentations, and immediately available for community exploration on interactive touchscreen displays.
Criteria Documentation and Communication
Maintaining accessible, clear criteria documentation prevents confusion and ensures consistent application across committee membership changes.
Written Criteria Documents
Create comprehensive written documents that:
Define every recognition category: Don’t assume shared understanding. Explicitly define what qualifies as “state championship participation,” “all-state recognition,” “school record holder,” and every other criterion.
Specify documentation requirements: What proof is required for each achievement type? Which sources are authoritative when records conflict?
Explain evaluation frameworks: If using scoring systems or evaluation matrices, publish complete scoring guides with point values and weighting rationales.
Document special considerations: How will committees address edge cases, tie scenarios, era differences, and contextual factors?
Establish amendment processes: Criteria evolve. Define processes for proposing, reviewing, and implementing criteria changes to prevent ad hoc modifications that create inconsistency.
Public Accessibility
Make criteria documentation publicly accessible through:
- School athletics website dedicated hall of fame sections
- Printed materials available in athletic offices
- Nomination form packages explaining standards
- Booster club and alumni association communications
- Digital display integrations where criteria are showcased alongside inductee profiles
Public accessibility serves multiple purposes—it manages nomination expectations, demonstrates program transparency, educates community members about achievement requirements, and provides objective reference points during selection discussions.
Schools implementing comprehensive digital recognition systems can integrate criteria documentation directly into interactive displays, allowing visitors to understand selection standards while exploring inductee profiles.
Implementing Digital Solutions for Comprehensive Recognition
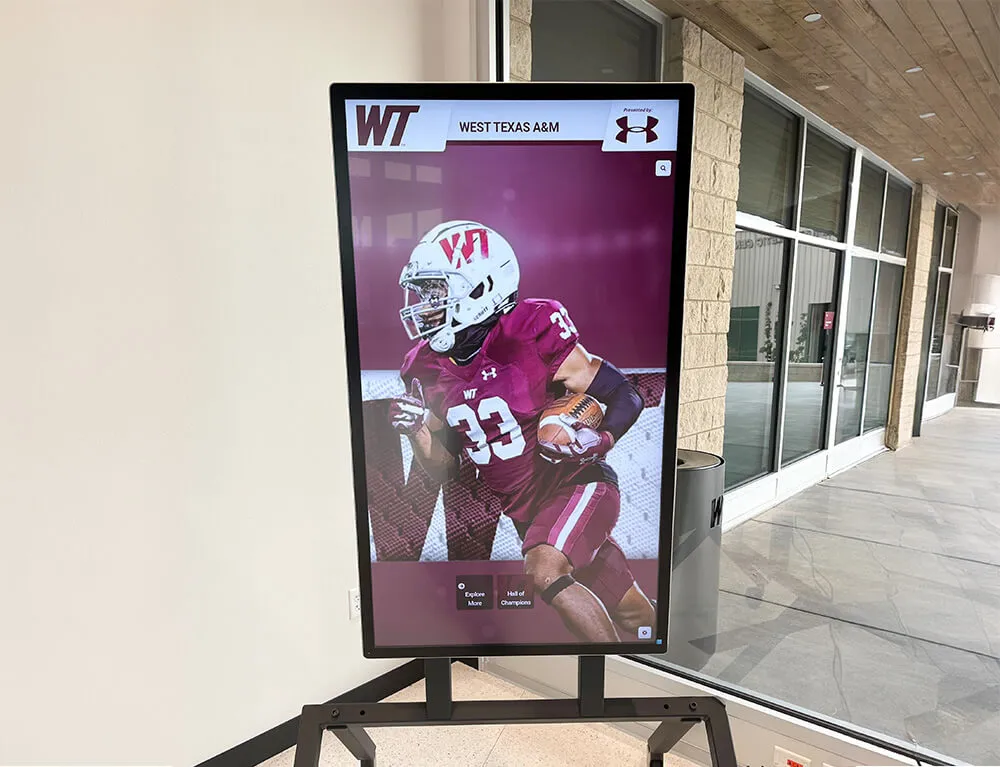
Traditional physical hall of fame displays face inherent limitations—finite space constraints force difficult decisions about who receives prominent recognition, static plaques limit information to brief name and achievement summaries, and updates require ongoing fabrication costs and physical modifications.
Modern digital recognition platforms address these fundamental limitations while enabling evaluation frameworks impossible with traditional approaches. When schools establish comprehensive selection criteria recognizing diverse achievement types across multiple sports and decades, digital systems provide the capacity to honor all deserving athletes without spatial compromises.
Unlimited recognition capacity: Digital platforms can showcase thousands of athletes with full biographical profiles, achievement documentation, and multimedia content—no need to choose between recognizing 50 or 500 inductees.
Searchable, filterable discovery: Visitors can explore inductees by sport, graduating class, achievement type, or championship year—or search directly for specific individuals—enabling personalized exploration impossible with static plaques.
Rich multimedia storytelling: Include photos, video highlights, statistical tables, career timelines, and coach testimonials that bring achievement stories to life beyond what text descriptions alone can convey.
Remote content management: Add new inductees, update existing profiles, correct errors, and enhance content instantly from any internet-connected device without requiring physical modifications or fabrication delays.
Web accessibility beyond campus: Alumni can explore hall of fame recognition from anywhere, share profiles via social media, and maintain meaningful connection with institutional achievement regardless of geographic distance.
Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions provide specialized platforms designed specifically for athletic recognition programs, with interfaces optimized for awards presentations, comprehensive achievement documentation, and integration with annual induction ceremonies.

Validation: Pre-Launch Criteria Audit
Before implementing your hall of fame program, complete this validation checklist ensuring criteria clarity and operational readiness.
Achievement Standards Documented
- All recognition categories clearly defined with specific achievement requirements
- Measurable thresholds established for each category (state championships, records, recognition levels)
- Sport-specific considerations documented for individual and team sports
- Historical era adjustment approaches defined
- Multi-sport athlete standards established
- Pioneer and trailblazer recognition criteria specified
- Coach and contributor recognition frameworks created
Selection Process Established
- Nomination procedures and eligibility timelines documented
- Selection committee composition and term limits defined
- Meeting schedules and deliberation processes established
- Voting procedures and required majorities specified
- Tie-breaking mechanisms documented
- Recusal protocols for conflict situations created
- Appeals or reconsideration processes defined
Documentation Requirements Created
- Achievement verification sources identified and prioritized
- Required supporting documentation specified for nominations
- Inductee profile content standards established
- Record-keeping systems and archives identified
- Photograph quality and rights requirements documented
- Statistical verification procedures established
Communication Frameworks Implemented
- Public criteria documentation published and accessible
- Nomination forms created with clear instructions
- Induction ceremony timing and format planned
- Announcement and recognition communication strategies developed
- Community education about standards and processes completed
- Digital or physical display specifications finalized
Sustainability Planning Completed
- Annual recognition cycle scheduled
- Multi-year implementation timeline created if building historical recognition
- Budget allocated for ongoing operations (ceremonies, displays, materials)
- Committee succession planning established
- Criteria review and amendment processes defined
- Technology or display maintenance plans created
This audit ensures comprehensive preparation, preventing common oversights that create operational problems after programs launch.
Moving Forward: Implementing Sustainable Recognition Excellence
Athletic directors and recognition committees who’ve reviewed this framework now have the tools to create defensible, sustainable hall of fame programs that honor achievement while maintaining community trust and institutional credibility.
Your immediate implementation steps:
Draft initial criteria documents using the frameworks and categories provided, customized for your program’s competitive context and institutional priorities.
Form your selection committee with diverse representation ensuring fair evaluation across sports, eras, and achievement types.
Define documentation standards specifying what information you’ll collect for each inductee and how you’ll verify achievement claims.
Select recognition display approach evaluating whether traditional physical displays or modern digital platforms best serve your long-term program needs.
Establish nomination processes creating accessible pathways for community members to suggest candidates while maintaining manageable administrative burden.
Plan inaugural induction ceremony creating memorable launch event that establishes program prestige and community excitement for annual recognition.
For schools seeking comprehensive recognition solutions that accommodate unlimited inductees with rich multimedia profiles, remote content management, and integration with academic achievement displays, digital platforms provide future-proof investments that grow with your programs over decades.
Build Your Hall of Fame Recognition Program with Professional Support
Rocket Alumni Solutions provides comprehensive hall of fame solutions designed specifically for athletic directors establishing or modernizing recognition programs. Our platform supports unlimited inductees with detailed profiles, multimedia content integration, intuitive search and filtering, remote content management, and accessibility features ensuring inclusive recognition.
We offer criteria development consultation, nomination process templates, selection committee frameworks, documentation standards guidance, and comprehensive training ensuring your recognition program honors achievement while maintaining operational sustainability. Whether you're recognizing decades of athletic tradition or launching new recognition initiatives, we'll help you implement systems that celebrate excellence effectively and efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions
Should we require minimum years since graduation before hall of fame eligibility?
Most programs implement 5-10 year waiting periods between graduation and hall of fame eligibility. Waiting periods serve several purposes: they ensure achievement represents sustained historical significance rather than recent memory bias, allow time for post-high school accomplishments that might enhance credentials, and provide perspective distinguishing truly exceptional careers from strong but not hall-of-fame-level achievement. However, truly exceptional accomplishments—Olympic medals, professional careers, national championships—sometimes merit immediate recognition. Document your standard waiting period while creating exceptional achievement provisions for rare cases warranting expedited consideration.
How do we handle athletes whose achievements span multiple sports with different success levels?
Multi-sport athletes present evaluation challenges when they achieved hall-of-fame-level success in one sport but participated without exceptional achievement in others. Most programs evaluate multi-sport athletes using their strongest sport achievements as primary criteria while considering multi-sport participation as contextual enhancement. For example, an all-state football player who also lettered in track receives credit for football achievement that qualifies them for hall of fame consideration, with multi-sport participation noted as additional accomplishment but not required for qualification. Alternatively, create specific multi-sport athlete criteria recognizing exceptional versatility as standalone achievement independent of single-sport excellence thresholds.
What happens when new records break existing hall of fame inductee achievements?
When current athletes break records held by hall of fame inductees, the original inductee typically remains recognized for their historical achievement while the new record holder becomes eligible for future consideration. Hall of fame recognition honors achievement within its era—the fact that records are subsequently broken doesn’t diminish the original accomplishment’s historical significance. Update record documentation to reflect current holders while maintaining historical recognition of previous record holders. This approach honors both past and present excellence while acknowledging athletic program progression. Digital recognition platforms excel at showing record progression timelines where visitors can explore how records evolved across program history.
Should we limit annual induction numbers to maintain prestige and avoid oversaturation?
Schools face tension between recognizing all deserving athletes and maintaining hall of fame prestige through selective admission. Moderate induction numbers (5-10 annually) typically maintain prestige while providing meaningful recognition volume. However, optimal numbers depend on program history and nomination quality. Schools with long athletic traditions and decades of unrecognized historical achievement might implement larger initial classes establishing historical recognition, then reduce to sustainable maintenance numbers. Others prefer pure achievement-based selection where any athlete meeting criteria thresholds receives recognition regardless of annual numbers. Document your approach—whether fixed numbers, flexible ranges, or achievement-based—and apply consistently to maintain community confidence in selection integrity.
How do we address selection disputes when committees choose not to induct nominated candidates?
Selection disputes are inevitable when emotional community members nominate athletes they personally remember fondly but whose objective achievements don’t meet documented standards. The best defense against dispute is transparent criteria and documentation. When committees choose not to induct nominees, document specific criteria gaps in confidential records—which achievement thresholds the nominee didn’t meet, what documentation was lacking, or how their accomplishments compared with current inductees. If disputes arise, committees can reference documented rationales rather than relying on memory. Consider establishing formal reconsideration processes where unsuccessful nominees can be renominated in future years with additional documentation, preventing permanent exclusion while maintaining selection standards. Crucially, keep committee deliberations confidential—discussing specific candidate weaknesses publicly creates community friction without serving productive purposes.
Can we recognize coaches and athletic directors in the same hall of fame as athletes?
Many programs successfully integrate coach and contributor recognition within athletic halls of fame by establishing separate criteria categories. Rather than competing with athletes using the same achievement standards, coaches receive evaluation based on coaching-specific accomplishments—championship teams coached, career win totals, athlete development success, and program building impact. Similarly, administrators, boosters, and contributors can receive recognition through service and impact criteria. The key is creating distinct evaluation frameworks for each category while maintaining comparable prestige levels. Some programs limit non-athlete inductions to one per annual class ensuring athlete focus remains primary while acknowledging exceptional non-athlete contributions. Document your approach to category balance and communicate clearly whether your hall of fame honors exclusively athletes or embraces broader athletic program contributors.
Additional Resources
Athletic directors establishing hall of fame programs may find value in related planning resources:
- Athletic Wall of Honor Implementation Guide - Alternative recognition formats and display configurations
- Digital Recognition Display Budget Calculator - Financial planning for recognition technology investments
- Championship Team Recognition Standards - Sport-specific achievement evaluation frameworks
- Sports Record Board Maintenance - Ongoing record documentation and display updates
- School Recognition Program Planning Timeline - Project planning and implementation scheduling
These resources provide complementary frameworks that athletic directors can adapt to their specific recognition program needs, creating comprehensive implementation toolkits for celebrating athletic excellence across multiple formats and recognition categories.