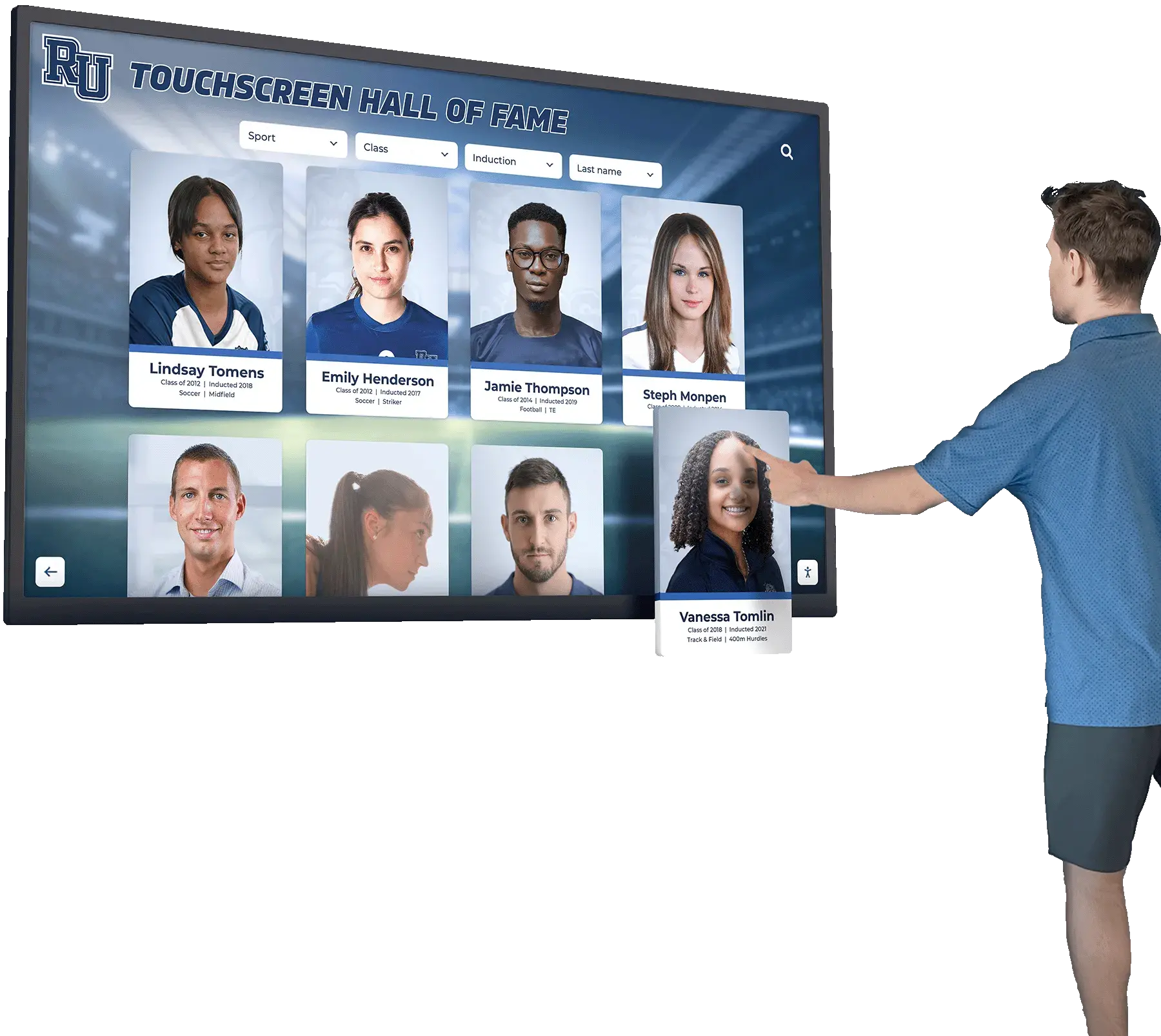
The cybersecurity skills gap continues to widen, with an estimated 3.5 million unfilled cybersecurity positions worldwide. As organizations scramble to build robust security teams, cybersecurity trainee recognition programs have emerged as a critical strategy for attracting, developing, and retaining the next generation of security professionals. Yet many organizations overlook the profound impact that meaningful recognition has on trainee success, career trajectory, and long-term retention in the cybersecurity field.
This comprehensive guide explores how to create effective recognition programs for cybersecurity trainees, interns, and apprentices—leveraging modern digital recognition technology to celebrate achievements, build confidence, and cultivate the security workforce your organization needs for the future.
Whether you’re managing a university cybersecurity program, running a corporate security training initiative, or developing apprenticeship pathways in the security field, strategic recognition transforms training experiences from transactional skill-building into transformative career development that builds lasting connections between trainees and your organization.

The Unique Recognition Needs of Cybersecurity Trainees
Cybersecurity trainees face distinct challenges that make recognition particularly important for their development and retention. Understanding these unique needs informs more effective recognition strategies.
Why Cybersecurity Trainees Need Recognition
Combating Imposter Syndrome in Technical Fields
Cybersecurity attracts highly motivated individuals who frequently experience imposter syndrome—the persistent feeling that they don’t belong or aren’t qualified despite evidence of competence. This phenomenon affects security professionals at all levels but hits trainees especially hard as they navigate complex technical concepts, rapidly evolving threats, and experienced colleagues who seem infinitely more knowledgeable.
Recognition serves as powerful external validation countering internal doubt:
- Formal acknowledgment of skills acquired and milestones achieved
- Public demonstration that leaders recognize trainee contributions
- Evidence contradicting feelings of inadequacy or fraudulence
- Confidence building that enables risk-taking essential for learning
- Belonging signals showing trainees they are valued community members
Building Confidence Through Visible Achievements
The cybersecurity field demands constant learning, technical mastery, and decisive action under pressure. Trainees building this confidence benefit tremendously from recognition that makes their growth visible:
- Certification achievements demonstrating technical competency
- Successful completion of capture-the-flag exercises and security challenges
- Contributions to vulnerability identification or threat detection
- Development of security tools, scripts, or automation
- Presentation of research findings or security analyses
When organizations celebrate these achievements visibly, trainees internalize evidence of their developing capabilities, building the confidence essential for security leadership.
Retention in Competitive Talent Markets
Organizations invest significant resources training security professionals, only to lose them to competitors offering higher salaries or better opportunities. While compensation matters, recognition creates emotional connections that pure salary increases cannot match:
- Trainees who feel valued are more likely to accept full-time positions
- Recognition builds organizational loyalty extending beyond transactional employment
- Visible appreciation differentiates employers in competitive recruiting environments
- Career development recognition demonstrates commitment to trainee growth
- Alumni networks formed through training programs support long-term recruitment

The Difference Between General and Cybersecurity-Specific Recognition
Generic employee recognition programs often miss elements particularly important for security trainees:
Traditional Recognition Limitations:
- Focus on business outcomes rather than technical skill development
- Emphasis on team harmony over individual technical achievement
- Recognition of tenure and attendance versus capability growth
- Limited understanding of security-specific accomplishments
- Generic praise without technical depth or specificity
- Celebration of conventional career paths only
Cybersecurity-Focused Recognition Advantages:
- Celebrates technical certifications and skill acquisitions
- Acknowledges contributions to organizational security posture
- Recognizes participation in competitions and challenges
- Values continuous learning and adaptation to emerging threats
- Demonstrates understanding of security domain complexities
- Supports diverse pathways into security careers
Effective cybersecurity trainee recognition requires domain awareness, technical understanding, and appreciation for the unique challenges security professionals face throughout their careers.
Building Comprehensive Cybersecurity Trainee Recognition Programs
Effective recognition programs acknowledge diverse contributions across the trainee journey, from initial onboarding through program completion and beyond.
Recognition Categories for Security Trainees
Technical Skill Milestones
Cybersecurity requires mastery of constantly evolving technical skills. Recognition should celebrate demonstrated competencies:
- Certification Achievements: CompTIA Security+, CEH, CISSP, OSCP, and other industry credentials
- Tool Proficiency: Mastery of security tools (Wireshark, Metasploit, Nmap, SIEM platforms)
- Programming Skills: Python, PowerShell, Bash scripting for security automation
- Cloud Security: AWS, Azure, or GCP security certification and implementation
- Specialized Domains: Network security, application security, forensics, threat intelligence
- Hands-On Capabilities: Penetration testing, vulnerability assessment, incident response
Organizations implementing digital recognition solutions can showcase these technical achievements with detailed profiles explaining the significance and requirements of each certification or skill milestone.
Competition and Challenge Success
Security competitions provide practical experience while building problem-solving capabilities:
- Capture the Flag (CTF) Events: Recognition for participants and top performers
- Bug Bounty Contributions: Acknowledgment of vulnerability discoveries
- Hackathons: Celebration of security tool development and innovation
- CyberPatriot Competitions: High school and collegiate team achievements
- Red Team/Blue Team Exercises: Performance in simulated attack-defense scenarios
- Security Awareness Challenges: Creating training materials or awareness campaigns
Competition success demonstrates practical application of security knowledge under realistic constraints, making it particularly valuable for recognition programs.
Threat Detection and Response Contributions
Even trainees can contribute meaningfully to organizational security:
- Identifying vulnerabilities during security assessments
- Detecting threats through log analysis or monitoring
- Contributing to incident response activities
- Developing or improving security documentation
- Creating automation scripts reducing manual security tasks
- Conducting security research benefiting the organization
Recognizing real-world security contributions reinforces that trainees provide value beyond their learning, strengthening their connection to organizational mission.

Professional Development Activities
Career growth extends beyond pure technical skills:
- Conference Participation: Attending DEF CON, Black Hat, RSA, or local security meetups
- Community Engagement: Contributing to security communities, forums, or open source projects
- Mentorship Roles: Helping newer trainees or students entering security
- Presentation Skills: Delivering briefings, workshops, or training sessions
- Writing and Documentation: Publishing security research, blog posts, or documentation
- Networking Achievement: Building professional relationships within security community
These activities develop well-rounded security professionals prepared for leadership roles beyond purely technical execution.
Structuring Recognition for Different Program Types
University Cybersecurity Programs
Academic programs preparing students for security careers should recognize:
- Outstanding academic performance in security coursework
- Research contributions to security knowledge
- Participation in university security competitions and clubs
- Summer internship placement and performance
- Capstone project excellence and real-world application
- Graduation and transition to security careers
Educational institutions can leverage interactive recognition displays showcasing alumni career paths, inspiring current students while demonstrating program success to prospective students and employers.
Corporate Internship Programs
Organizations running security internships should celebrate:
- Successful completion of onboarding and training phases
- Project deliverables and technical contributions
- Collaboration with full-time security team members
- Participation in lunch-and-learn sessions and workshops
- Conversion to full-time employment offers
- Intern alumni returning as experienced professionals
Corporate programs benefit from recognition extending beyond individual program cohorts, building multi-year narratives of organizational commitment to workforce development.
Apprenticeship and Alternative Pathway Programs
Programs supporting non-traditional entry into cybersecurity should recognize:
- Completion of foundational technical training modules
- Progression through structured competency frameworks
- Transition from entry-level to specialized security roles
- Achievement by individuals from underrepresented backgrounds
- Career changes demonstrating security as accessible to diverse backgrounds
- Multi-year career progression from apprentice through experienced professional
These programs particularly benefit from storytelling through digital recognition, showcasing diverse pathways that inspire others considering security careers from non-traditional backgrounds.
Implementing Digital Recognition for Security Training Programs
Modern digital recognition displays provide powerful tools for celebrating trainee achievements while supporting program objectives.
Advantages of Digital Recognition for Security Programs
Showcasing Technical Competencies Visually
Digital platforms enable rich presentation of technical achievements:
Interactive Certification Displays
Showcase certification badges, exam scores, and technical competencies with detailed explanations helping non-technical viewers understand significance.
Video Demonstrations
Include screencasts or presentations showing trainees explaining technical concepts, demonstrating their communication skills alongside technical knowledge.
Project Portfolios
Present security projects, code samples, and technical documentation in interactive galleries allowing detailed exploration.
Timeline Visualizations
Display trainee progression through programs, certifications, and skill development in intuitive visual timelines.
Real-Time Updates Supporting Program Momentum
Training programs benefit from immediate recognition:
- Certification achievements announced within days of completion
- Competition results shared immediately following events
- Project completions celebrated as teams deliver work
- Weekly or monthly highlights maintaining consistent recognition
- Dynamic content keeping displays current and relevant
The ability to update digital displays instantly without production delays or physical installation ensures recognition remains timely and impactful.
Extending Recognition Beyond Physical Locations
Security training programs often involve distributed teams, remote participants, and alumni scattered geographically:
- Web-accessible platforms enabling recognition viewing from anywhere
- Social media integration allowing trainees to share achievements
- Mobile optimization ensuring access on smartphones and tablets
- QR codes connecting physical displays to online profiles
- Integration with alumni networks and professional communities
This extended reach amplifies recognition impact far beyond physical display locations.

Content Strategies for Security Trainee Recognition
Profile Components Maximizing Impact
Effective trainee profiles include:
Core Information:
- Professional headshot or preferred photo
- Current role and program cohort
- Geographic location and institution/organization
- Brief biographical background
Achievement Highlights:
- Certifications earned with dates and issuing organizations
- Competition results and rankings
- Projects completed with descriptions and impact
- Skills developed and technical competencies demonstrated
- Mentors and leaders who supported development
Personal Narrative:
- Path into cybersecurity (especially valuable for non-traditional backgrounds)
- Challenges overcome during training
- Career aspirations and future goals
- Advice for future trainees
- What recognition means personally
Multimedia Elements:
- Technical presentations or demonstrations
- Photos from competitions, conferences, or team events
- Scanned certificates and credentials
- Code samples or technical documentation (when appropriate)
These comprehensive profiles tell complete stories rather than simply listing credentials, creating emotional connections with viewers.
Integration with Existing Training Infrastructure
Digital recognition systems should connect seamlessly with program operations:
Learning Management System (LMS) Integration
- Automatic recognition when courses or certifications complete
- Skill badges earned within training platforms displayed in recognition profiles
- Progress tracking synchronized between systems
- Reduced administrative burden through automation
Certification Tracking Systems
- Direct feeds from certification databases
- Validation of credentials through official verification
- Expiration tracking and renewal recognition
- Comprehensive certification history maintenance
Competition Platforms
- Integration with CTF scoring systems
- Automatic recognition of top performers
- Team achievement tracking and acknowledgment
- Historical competition results and trends
Organizations can explore best software solutions for education records to understand integration capabilities supporting automated recognition workflows.
Location and Placement Strategies for Security Training Programs
Strategic placement of recognition displays maximizes visibility and impact within organizations and educational institutions.
Optimal Placement for Maximum Impact
Training Facilities and Labs
Primary training locations provide natural recognition settings:
- Security Operations Centers (SOCs): Displays showcasing trainee contributions to threat detection
- Training Classrooms: Recognition visible to current cohorts, inspiring achievement
- Computer Labs: Displays celebrating technical accomplishments in hands-on learning environments
- Break Rooms: Informal viewing during downtime and social interactions
High-Traffic Common Areas
Broader visibility amplifies recognition value:
- Main lobbies welcoming visitors, candidates, and stakeholders
- Cafeterias and common areas with diverse audience exposure
- Conference rooms where trainee accomplishments impress partners and clients
- Corridor intersections with maximum pedestrian traffic
Recruitment and Onboarding Spaces
Recognition supporting pipeline development:
- Recruitment centers demonstrating program success to prospective trainees
- Onboarding areas inspiring new cohorts with predecessor achievements
- Career fairs and recruiting events (mobile displays or digital presentations)
- Open house events showcasing program impact to families and communities
Virtual and Hybrid Placement
Modern programs require digital-first approaches:
- Program websites featuring searchable trainee databases
- Virtual lobby displays for remote participants
- Integration with internal communication platforms
- Social media channels amplifying recognition reach

Building Recognition Programs That Scale
Sustainable recognition programs grow naturally with training initiatives without creating administrative burden.
Establishing Sustainable Processes
Clear Nomination and Selection Criteria
Transparent processes ensure fairness and consistency:
- Published criteria for each recognition category
- Objective metrics where possible (certifications, competition rankings)
- Subjective evaluation guidelines for qualitative contributions
- Nomination processes allowing peer, mentor, and self-nomination
- Review committees ensuring diverse perspective representation
- Appeal or reconsideration processes for fairness
Content Development Workflows
Efficient processes prevent recognition delays:
- Standardized profile templates requiring specific information
- Photo guidelines ensuring quality and consistency
- Approval workflows with defined timelines (48-72 hours)
- Self-service submission allowing trainee participation
- Bulk processing capabilities for cohort recognition
- Scheduled publication dates aligning with program milestones
Organizations managing multiple training programs benefit from content planning strategies that ensure consistent quality across recognition initiatives.
Regular Recognition Rhythms
Predictable schedules maintain momentum:
- Weekly: Highlight recent achievements, certifications, or competition results
- Monthly: Feature spotlight trainees with comprehensive profiles
- Quarterly: Cohort completions and major program milestones
- Annually: Program retrospectives and year-end celebrations
- Real-time: Competition results and time-sensitive announcements
Measuring Recognition Program Impact
Systematic assessment demonstrates value and guides improvement:
Trainee Satisfaction Metrics
- Post-program surveys asking about recognition experiences
- Exit interviews with completing trainees
- Comparison of recognized versus non-recognized trainee retention
- Net Promoter Score (NPS) for program recommendations
- Social media sharing and engagement rates
Recruitment and Pipeline Metrics
- Application quality and volume trends
- Recognition program visibility during recruiting
- Candidate feedback about program reputation
- Trainee referrals of friends and colleagues
- Diversity metrics for applicant pools
Retention and Career Progression
- Conversion rates from trainee to full-time employment
- Recognition correlation with job offer acceptance
- Career advancement of program alumni
- Alumni engagement with organization long-term
- Mentorship and giving-back behaviors
Organizational Impact
- Reduced time-to-fill for security positions
- Cost savings from internal pipeline versus external recruiting
- Quality improvements in security team capabilities
- Recognition program ROI calculations
- Leadership satisfaction with program outcomes
Organizations seeking data-driven approaches can explore advanced analytics for digital recognition to quantify program value.
Inclusive Recognition Supporting Diverse Cybersecurity Pipelines
The cybersecurity workforce diversity gap demands intentional recognition strategies supporting underrepresented groups entering security careers.
Addressing Representation Through Recognition
Showcasing Diverse Career Pathways
Recognition should celebrate various routes into cybersecurity:
- Career changers from non-technical backgrounds
- Military veterans transitioning to civilian security roles
- Self-taught professionals without formal degrees
- Individuals from historically underrepresented demographics
- International talent bringing global perspectives
- Neurodiverse individuals with unique security insights
Visible diversity in recognition programs signals that security careers are accessible to all, not just those following traditional computer science pathways.
Overcoming Stereotype Threat
Underrepresented trainees often experience stereotype threat—concern that their performance confirms negative group stereotypes. Recognition combats this by:
- Providing concrete evidence of belonging and capability
- Showcasing successful professionals who share backgrounds
- Normalizing diverse presence in security leadership
- Creating role models for future underrepresented trainees
- Building confidence through public validation
Building Inclusive Communities Through Recognition
Programs should intentionally:
- Recognize contributions to diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives
- Celebrate participation in affinity groups and support organizations
- Acknowledge mentorship of underrepresented trainees
- Highlight leadership in accessibility and inclusion advocacy
- Feature alumni supporting diversity in security field
Organizations committed to inclusive digital recognition create environments where all trainees see themselves represented and valued.
Accessibility Considerations
Recognition systems must be accessible to trainees with disabilities:
- Physical Accessibility: ADA-compliant display mounting and approach space
- Visual Accommodations: High-contrast modes, screen readers, text magnification
- Auditory Options: Captions for video content and audio alternatives
- Cognitive Considerations: Simplified navigation and clear information hierarchy
- Language Support: Multilingual capabilities for international programs
Accessible recognition demonstrates organizational commitment to inclusion extending beyond rhetoric to practical implementation.

Connecting Recognition to Career Development
The most powerful trainee recognition programs extend beyond celebration to actively supporting career advancement.
Recognition as Career Development Tool
Building Professional Portfolios
Digital recognition profiles serve as career documentation:
- Comprehensive records of achievements and capabilities
- Evidence supporting resume claims and interview discussions
- Shareable links for job applications and networking
- Professional development timeline visualization
- Skill demonstrations through projects and presentations
Trainees can leverage recognition profiles as living portfolios throughout careers, with organizations supporting long-term professional success.
Networking and Mentorship Facilitation
Recognition creates connection opportunities:
- Alumni networks built around shared program experiences
- Mentorship connections between current and former trainees
- Employer visibility into talent pipeline capabilities
- Professional relationship development through recognition events
- Community building among cohorts and across years
These networks provide career support extending long after formal training concludes.
Credential Verification and Background
Digital recognition offers practical benefits:
- Verified credential databases supporting employment screening
- Reduced resume fraud through authenticated achievements
- Quick reference for hiring managers evaluating candidates
- Historical records supporting security clearance processes
- Continuing education tracking for certification maintenance
Recognition Integration with Hiring Processes
Organizations can strategically connect recognition to employment:
Internal Recruiting Advantage
- Recognition profiles provide detailed candidate information
- Hiring managers see trainee capabilities demonstrated
- Cultural fit assessment through program participation
- Reduced interview requirements for known quantities
- Streamlined onboarding for already-familiar trainees
External Recruiting Support
- Recognition demonstrates organizational investment in development
- Program alumni provide authentic employer brand advocacy
- Partner organizations identify talent through recognition showcases
- Industry visibility positions organization as development leader
- Recognition supports diversity recruiting initiatives
Organizations managing college recruitment programs can extend similar strategies to cybersecurity talent pipelines.
Recognition for Virtual and Hybrid Training Programs
Modern security training increasingly occurs remotely, requiring recognition strategies adapting to distributed environments.
Digital-First Recognition Approaches
Virtual Display Strategies
Remote programs need creative recognition delivery:
- Web platforms as primary recognition medium
- Virtual ceremony events celebrating achievements
- Social media campaigns highlighting trainee success
- Email spotlights featuring recognized individuals
- Digital badges for social media profiles
- Mobile apps providing recognition access anywhere
Maintaining Connection Without Physical Presence
Remote trainees particularly need belonging signals:
- Virtual cohort communities built around recognition
- Online galleries celebrating distributed team achievements
- Video testimonials from recognized trainees
- Live-streamed recognition events with interactive elements
- Alumni networks connecting across geographic boundaries
Hybrid Model Considerations
Programs combining in-person and remote elements should:
- Ensure equivalent recognition for all participants
- Provide both physical and digital recognition access
- Avoid creating perceived hierarchies between modalities
- Celebrate unique advantages of hybrid participation
- Document recognition in formats accessible to all
Organizations exploring virtual recognition platforms can identify solutions supporting distributed training programs effectively.
Best Practices for Cybersecurity Trainee Recognition
Successful programs share common characteristics informed by experience across diverse organizations and educational institutions.
Essential Success Factors
Authenticity and Sincerity
Recognition must be genuine:
- Specific descriptions of achievements rather than generic praise
- Demonstrated understanding of technical accomplishments
- Proportionate recognition matching achievement significance
- Consistency preventing favoritism perceptions
- Leaders personally engaging with recognition, not delegating entirely
Trainees immediately recognize insincere recognition, which damages culture rather than strengthening it.
Timely Recognition Delivery
Delays diminish impact:
- Certification recognition within one week of achievement
- Competition results announced immediately following events
- Project completion celebrated promptly upon delivery
- Real-time recognition for significant contributions
- Annual recognition occurring at natural program milestones
Organizational commitment to content management efficiency enables timely recognition without administrative burden.
Balance Individual and Team Recognition
Security work involves both:
- Individual technical achievements and certifications
- Team-based projects and collaborative success
- Peer support and mentorship contributions
- Solo competition performance and team events
- Leadership within groups and individual initiative
Programs recognizing both dimensions support well-rounded professional development.
Connection to Organizational Values
Recognition should reinforce culture:
- Alignment with organizational security priorities
- Embodiment of institutional values and ethics
- Support for diversity and inclusion commitments
- Demonstration of learning and growth mindsets
- Emphasis on integrity and professional responsibility
Values-aligned recognition strengthens culture while celebrating achievement.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Over-Recognition Diluting Meaning
Excessive recognition reduces impact:
- Maintain selectivity preserving significance
- Ensure achievements merit formal recognition
- Avoid participation trophies undermining merit-based celebration
- Reserve highest honors for exceptional contributions
- Balance accessibility with meaningful standards
Neglecting Recognition After Initial Implementation
Many programs start strong but fade:
- Establish sustainable processes from the beginning
- Assign clear responsibility and accountability
- Integrate recognition into normal operational rhythms
- Schedule regular content reviews and updates
- Maintain executive sponsorship and organizational priority
Focusing Exclusively on Technical Skills
Complete professionals require broader capabilities:
- Recognize communication and presentation skills
- Celebrate teamwork and collaboration
- Acknowledge leadership and mentorship
- Value creativity and innovative thinking
- Honor ethical behavior and professional responsibility
Technical expertise matters, but comprehensive recognition develops well-rounded security professionals.
Transform Your Security Training Recognition
Discover how digital recognition displays can elevate your cybersecurity training program, strengthen trainee engagement, and build the security workforce pipeline your organization needs for the future.
Schedule Your ConsultationConclusion: Recognition as Strategic Workforce Development
Cybersecurity trainee recognition programs are not optional extras or nice-to-have cultural initiatives—they are strategic investments in workforce development addressing the critical security skills shortage affecting organizations worldwide. As competition for security talent intensifies, organizations that recognize and celebrate trainee achievements build competitive advantages in attracting, developing, and retaining the cybersecurity professionals essential for protecting digital assets and infrastructure.
Key Strategic Benefits:
Talent Pipeline Development Recognition programs create visible pathways into cybersecurity careers, attracting diverse candidates who see themselves represented in successful alumni and current trainees.
Retention and Conversion Trainees who feel valued and recognized choose to accept full-time positions, reducing recruiting costs while ensuring cultural fit and demonstrated capability.
Reputation and Brand Positioning Organizations known for meaningful recognition become employers of choice in competitive talent markets, attracting higher-quality applicants and reducing recruiting challenges.
Career Development Support Recognition extending beyond program completion supports long-term career success, creating alumni networks that strengthen organizational connections and recruiting pipelines for years.
Cultural Differentiation In fields where compensation varies less across employers, recognition culture differentiates organizations competing for the same talent pool.
For organizations ready to elevate cybersecurity training programs beyond transactional skill-building to transformative career development, modern digital recognition technology provides scalable, engaging platforms that celebrate achievements while supporting strategic workforce development objectives.
By implementing comprehensive recognition programs that honor diverse contributions, celebrate technical and professional growth, and create visible career pathways, organizations invest in the security workforce of tomorrow while addressing today’s critical talent shortage. The combination of thoughtful recognition strategy with powerful digital platforms creates programs that attract talent, build capability, strengthen retention, and position organizations as leaders in cybersecurity workforce development.
Whether launching new training initiatives or enhancing existing programs, strategic recognition should be central to planning—not an afterthought added once programs are operational. Organizations that embed recognition into program DNA from the beginning build stronger cultures, achieve better outcomes, and create lasting competitive advantages in the ongoing battle for cybersecurity talent.