Statewide halls of fame represent some of the most prestigious forms of recognition in America, celebrating extraordinary achievements that transcend individual institutions to honor excellence across entire states. From athletic prowess and academic achievement to artistic contributions and community service, these recognition programs preserve legacies, inspire future generations, and unite communities through shared celebration of accomplishment.
This comprehensive guide explores how statewide halls of fame operate, the unique challenges they address, and how modern digital recognition solutions enable these programs to engage audiences more effectively while preserving state heritage for generations to come.
Statewide halls of fame differ fundamentally from institutional recognition programs. While schools, universities, and organizations celebrate achievements within their specific communities, statewide programs must balance representation across geographic regions, demographic groups, achievement categories, and time periods while maintaining rigorous standards that justify state-level honor.

Statewide recognition programs unite communities through celebration of collective excellence
Understanding Statewide Hall of Fame Programs
Statewide halls of fame serve critical functions in preserving state heritage and honoring exceptional individuals whose contributions extend beyond local communities to impact entire states or the nation.
The Purpose and Impact of State-Level Recognition
Recognition at the state level carries unique prestige. Unlike local or institutional honors that celebrate achievement within limited contexts, statewide induction acknowledges contributions that shaped state identity, influenced multiple communities, or achieved national prominence while maintaining strong state connections.
These programs preserve important historical records about individuals who might otherwise be forgotten. They document the evolution of various fields across states, create educational resources about state heritage, and inspire current residents by demonstrating that extraordinary achievement remains possible regardless of background or origin.
Many statewide halls of fame focus on specific domains. Athletic halls of fame honor sports legends who brought glory to their states through championship performances, Olympic representation, or professional careers. Arts and entertainment halls celebrate musicians, actors, writers, and artists whose creative work carried state influence nationally. Business and innovation halls recognize entrepreneurs and inventors whose ventures created economic impact and employment. Academic halls honor educators, researchers, and scholars whose intellectual contributions advanced knowledge.
Common Structures and Governance Models
Most statewide halls of fame operate as independent nonprofit organizations, though some function under state government oversight or affiliate with universities and historical societies. This organizational structure significantly influences program operations, funding sources, selection processes, and public accessibility.
Independent nonprofit halls typically rely on membership fees, private donations, event revenues, corporate sponsorships, and merchandise sales. Board governance includes representatives from across states ensuring geographic and demographic diversity. Selection committees often comprise former inductees, subject matter experts, media representatives, and community leaders who bring varied perspectives to evaluation processes.
State-affiliated programs may receive appropriations from state budgets alongside private fundraising, benefit from facility space in state buildings or museums, leverage state marketing channels for promotion, and align selection with state historical preservation goals. However, they may face political considerations affecting operations and experience budget constraints during economic downturns.

Statewide programs balance tradition with modern recognition technology
Geographic and Demographic Representation Challenges
Statewide halls face ongoing challenges ensuring fair representation across diverse populations. Urban areas often produce more recognized achievers due to larger populations and greater resources, while rural communities may feel underrepresented despite significant contributions. Different regions within states may have distinct cultural traditions and achievement patterns requiring acknowledgment.
Demographic representation proves equally critical. Historical halls often reflect the biases of their founding eras, with women, minorities, and marginalized communities significantly underrepresented. Contemporary programs must address these inequities through proactive outreach to identify overlooked candidates, revised criteria emphasizing diverse achievement types, and education about historical context explaining representation gaps.
Many successful programs implement policies ensuring selection processes actively consider candidates from underrepresented groups and time periods, establish minimum representation targets for various demographics and regions, partner with community organizations to identify qualified candidates, and conduct regular audits of inductee demographics to identify representation gaps.
Categories of Statewide Hall of Fame Programs
Statewide recognition spans numerous achievement domains, each with unique characteristics and selection considerations.
Athletic Halls of Fame
Sports halls represent the most common statewide recognition category. These programs typically honor high school, college, and professional athletes who achieved state, national, or international distinction, coaches who developed championship programs or influenced athletic development across states, teams that achieved extraordinary success or historical significance, and contributors including officials, administrators, and supporters who advanced athletics.
Selection criteria often emphasize measurable achievements such as state championships, All-American honors, professional contracts, Olympic participation, and coaching records. However, the best programs also consider character, sportsmanship, positive role modeling, contributions to athletic development, and long-term impact on communities—as explored in our guide on athletic wall of honor recognition.
Many states maintain separate halls for different sports or levels. California, Texas, and Florida, for instance, operate multiple athletic halls addressing high school sports, college athletics, and professional achievements separately. This specialization allows more focused recognition while enabling deep documentation of specific athletic traditions and histories.

Athletic halls preserve records of sporting excellence across generations
Arts, Music, and Entertainment Recognition
Statewide recognition of creative achievement celebrates individuals whose artistic work achieved national or international prominence, influenced artistic movements or genres, brought recognition to states through creative excellence, mentored emerging artists or advanced arts education, or preserved cultural traditions and heritage.
These halls face unique challenges as artistic merit often proves more subjective than athletic achievement. Selection committees typically include practicing artists, critics and historians with expertise in relevant fields, arts educators and administrators, and representatives from arts organizations and institutions. This diverse composition helps ensure balanced evaluation considering multiple perspectives on artistic significance.
Many programs organize recognition by discipline—visual arts, music, literature, theater, film—while others maintain integrated halls celebrating all creative fields. The organizational approach influences content presentation, as discipline-specific halls enable deeper context about artistic movements and technical evolution within fields.
Business, Innovation, and Entrepreneurship Halls
Recognition of business achievement honors individuals whose ventures created significant employment and economic impact, developed innovative products or services, demonstrated ethical leadership and corporate citizenship, contributed philanthropically to communities, or influenced business practices and standards.
These programs must balance celebrating success with acknowledging that business achievement often involves privilege and resources unavailable to all residents. The most thoughtful programs emphasize innovation, ethical leadership, and community contribution rather than purely financial success, recognize diverse business types including small businesses and social enterprises, acknowledge teamwork and employee contributions to success, and contextualize achievements within economic and social conditions of their eras.
Selection criteria might include objective measures like jobs created, revenue generated, patents obtained, or awards received, alongside qualitative factors such as innovation demonstrated, leadership quality, ethical standards maintained, and community contributions made.

Business halls celebrate entrepreneurship and innovation driving state economies
Academic and Educational Excellence
Academic halls honor educators who influenced thousands of students across careers, advanced educational practices or curricula, demonstrated exceptional teaching excellence, or led institutions to prominence, along with scholars whose research advanced knowledge in fields, earned national or international recognition, mentored future researchers and academics, or applied research to address practical challenges.
Recognition of educational achievement requires understanding that academic impact often manifests gradually rather than through dramatic moments. The effects of excellent teaching or groundbreaking research may not become fully apparent for years or decades. Selection committees must therefore evaluate long-term influence and legacy rather than only immediate recognition or short-term outcomes.
These programs often partner with state education departments, university systems, and teaching associations to identify qualified candidates and ensure recognition reflects diverse educational contexts from early childhood through higher education and adult learning across public, private, and alternative educational settings.
Selection Processes and Criteria
Rigorous, transparent selection processes maintain hall of fame credibility and ensure recognition retains prestige and meaning.
Establishing Clear Eligibility Requirements
Most statewide halls establish objective eligibility thresholds that candidates must meet before qualitative evaluation begins. Common requirements include minimum time since achievement or retirement to ensure lasting impact, strong documented connections to states through birth, residence, or career, achievement levels exceeding local or regional significance, and character standards reflecting positive values.
Time requirements typically range from three to ten years post-achievement or retirement. This waiting period allows thorough assessment of lasting impact and prevents recognition based on temporary success or fleeting fame. Some programs make exceptions for extraordinary circumstances such as deceased candidates or those facing terminal illness.
State connection requirements vary significantly. Some halls require birth within states, while others accept individuals who spent significant portions of careers or lives in states even if born elsewhere. These policies significantly influence inductee demographics, as restrictive residency requirements may exclude notable individuals with important state connections who spent portions of careers elsewhere.

Rigorous selection processes maintain recognition program credibility
Nomination and Evaluation Procedures
Transparent nomination processes allow public participation while maintaining quality control. Most programs accept nominations from anyone with appropriate supporting documentation, require standardized forms ensuring consistent information, establish submission deadlines creating predictable evaluation cycles, and provide guidelines about what evidence strengthens nominations.
Nomination packages typically include biographical information and achievement summaries, documentation of accomplishments through records, articles, or awards, letters of support from colleagues, competitors, or community members, visual materials such as photographs or performance footage, and personal statements from candidates when possible addressing their legacies and values.
Selection committees then evaluate nominations through multiple review rounds. Initial screening verifies eligibility and completeness, detailed evaluation assesses achievement significance against established criteria, comparative analysis considers candidates relative to previous inductees and each other, and final deliberation produces induction class recommendations for board approval.
Balancing Objective Metrics with Subjective Assessment
The tension between quantifiable achievement and qualitative impact challenges all halls of fame. Athletic programs can rely partly on statistics and championships, but must also evaluate intangibles like leadership and sportsmanship. Arts programs face even greater subjectivity, as aesthetic merit and cultural impact resist simple quantification.
Successful programs develop detailed rubrics that committees use to evaluate candidates consistently. These frameworks typically organize criteria into weighted categories such as achievement magnitude measured through awards, recognition, and documented impact, longevity considering sustained excellence over time rather than brief peaks, influence on fields and future generations, character and values demonstrated throughout careers and lives, and state connections including duration and depth of state associations.
Committee deliberations combine individual scoring with group discussion, allowing quantitative assessment to inform but not fully determine decisions. This balanced approach acknowledges that while numbers provide important context, they cannot capture complete significance of human achievement and contribution.
Physical and Digital Recognition Strategies
Statewide halls employ varied approaches to make recognition accessible to geographically dispersed populations.
Traditional Physical Hall Locations
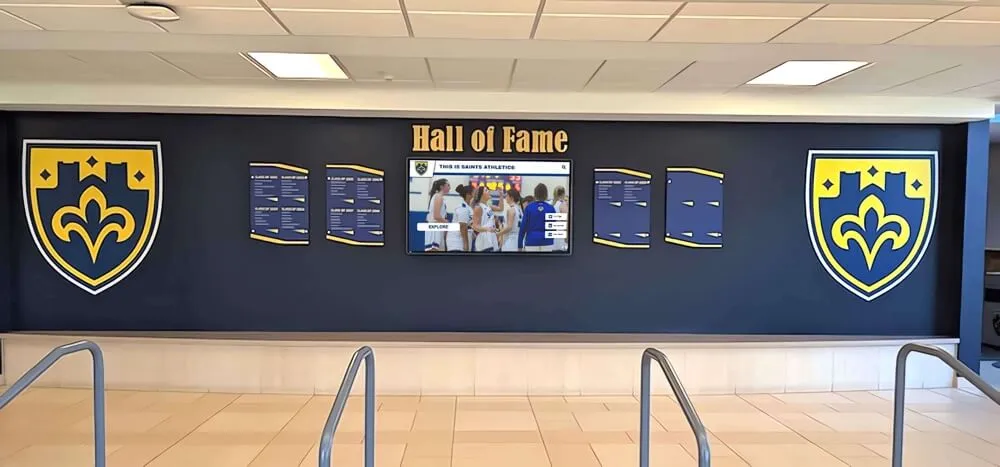
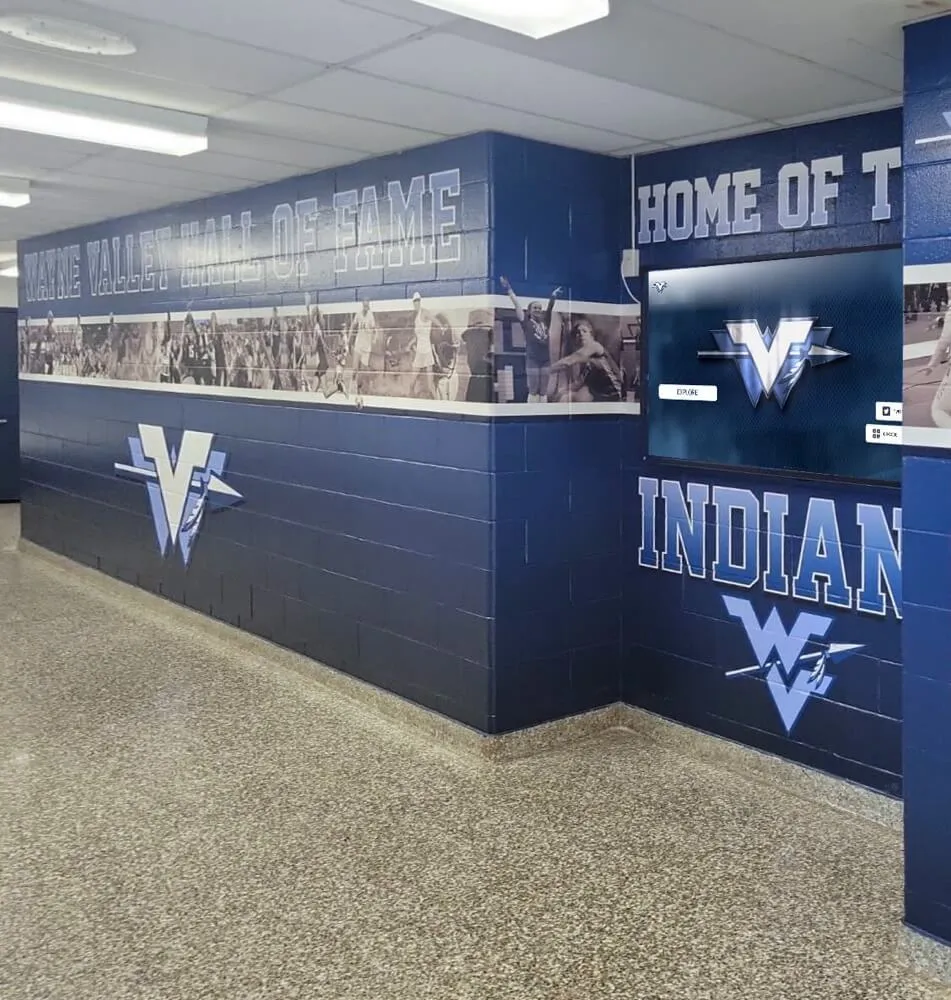
Many established halls maintain permanent physical locations featuring exhibits about inductees. These facilities typically include wall displays with plaques and photographs, trophy cases and artifact displays, multimedia stations with video content, interactive elements allowing visitor exploration, and event spaces for inductions and programs.
Physical locations serve important functions as pilgrimage destinations for fans and families, educational resources for school groups and tourists, event venues for ceremonies and fundraisers, and archives preserving historical artifacts and documents. However, they face significant limitations including accessibility only to those who can visit physical sites, maintenance costs for buildings and exhibits, static content requiring expensive updates, and limited capacity for comprehensive recognition of all inductees.
Location selection proves critical for physical halls. Some states establish halls in capital cities for symbolic significance and tourist traffic, while others choose locations with historical relevance to recognized achievements. Rural locations may face visitor volume challenges despite lower costs, while urban placements increase accessibility but raise operational expenses—similar to considerations discussed in our guide on hall of fame wall design.

Physical halls create destination experiences for fans and families
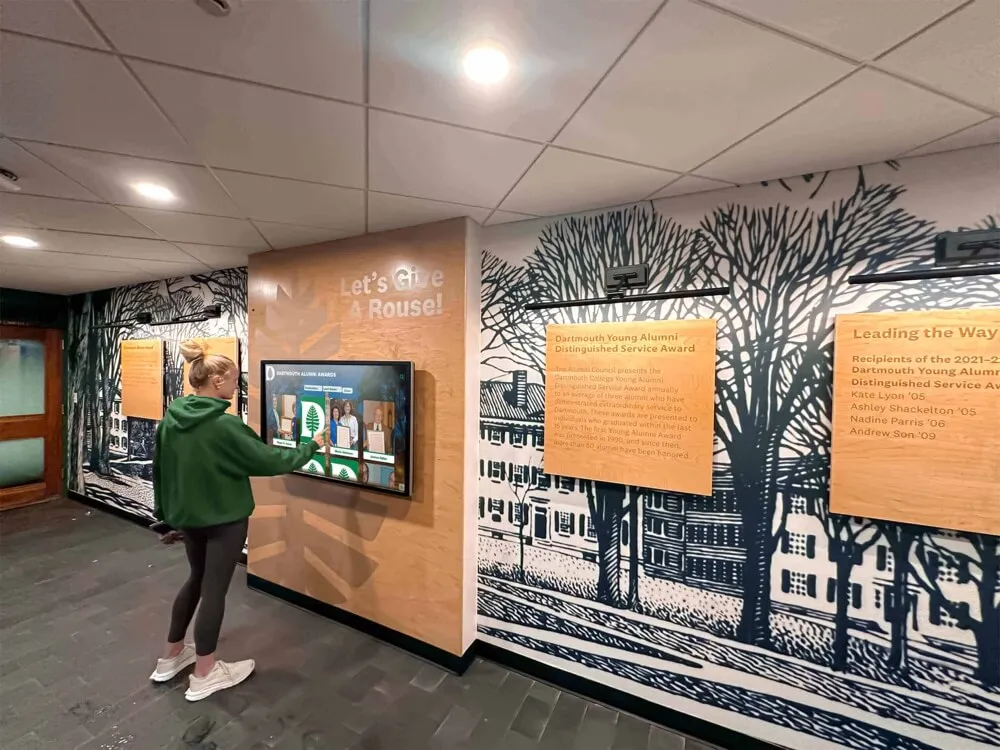
Digital Recognition Platforms Extending State Access
Digital technology transforms how statewide halls reach populations. Online platforms eliminate geographic barriers, allowing anyone with internet access to explore recognition regardless of location. Digital systems provide unlimited capacity for comprehensive profiles, rich multimedia content impossible in physical displays, powerful search and filtering tools, regular updates maintaining current information, and analytics revealing engagement patterns.
Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions enable statewide halls to create comprehensive digital recognition accessible throughout states and beyond. These platforms support detailed athlete or artist profiles with photos, videos, and documents, searchable databases allowing visitors to find specific individuals quickly, mobile-responsive designs working on all devices, social sharing features amplifying recognition reach, and content management systems enabling easy updates.
Some halls maintain hybrid approaches with physical locations complemented by robust digital platforms. This strategy preserves traditional destination experiences while extending access digitally. Visitors exploring physical exhibits can access additional online content through QR codes, while those unable to visit facilities can experience recognition remotely through comprehensive digital access.
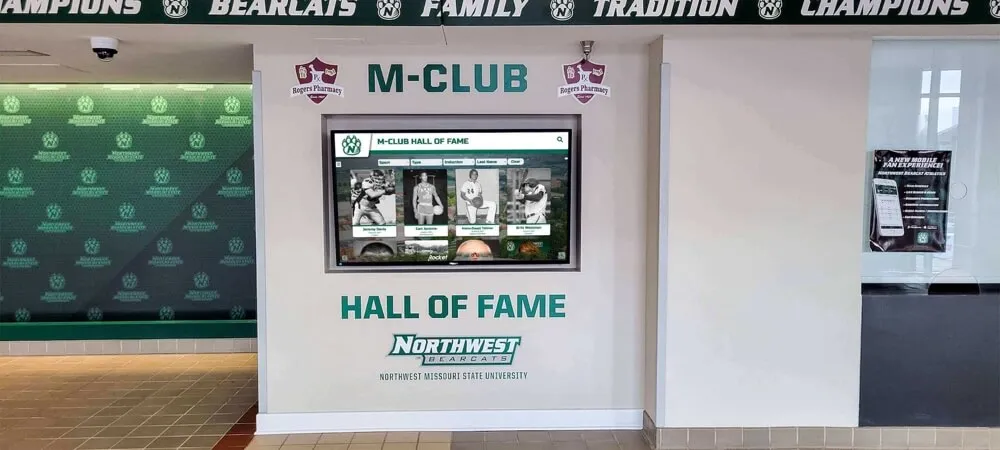
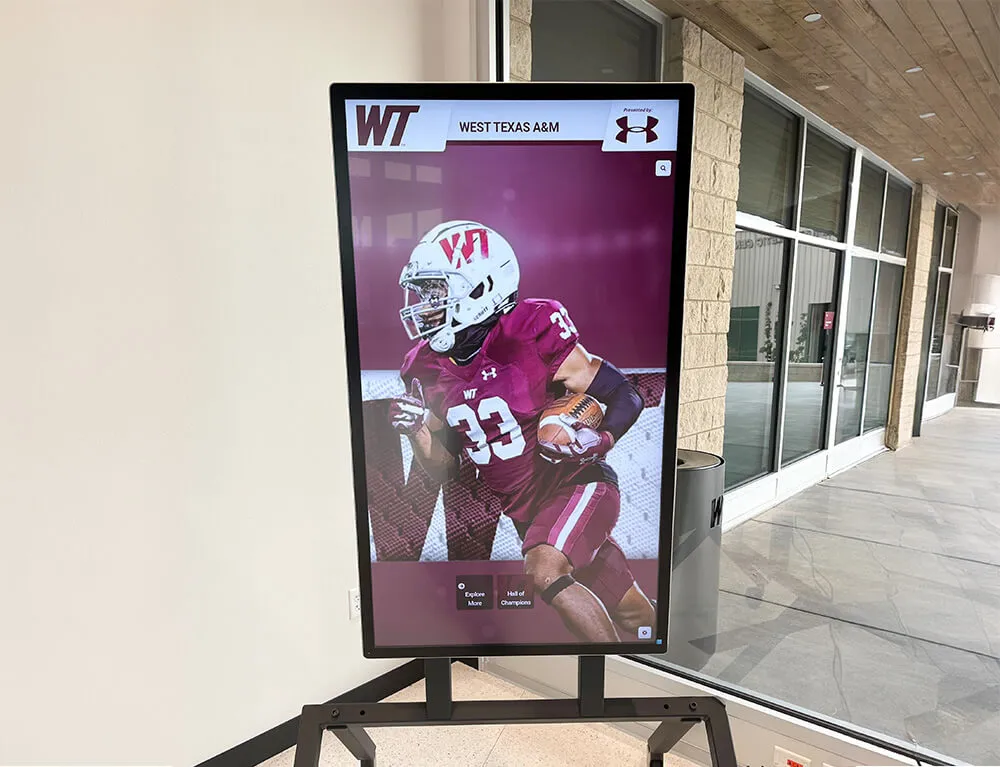
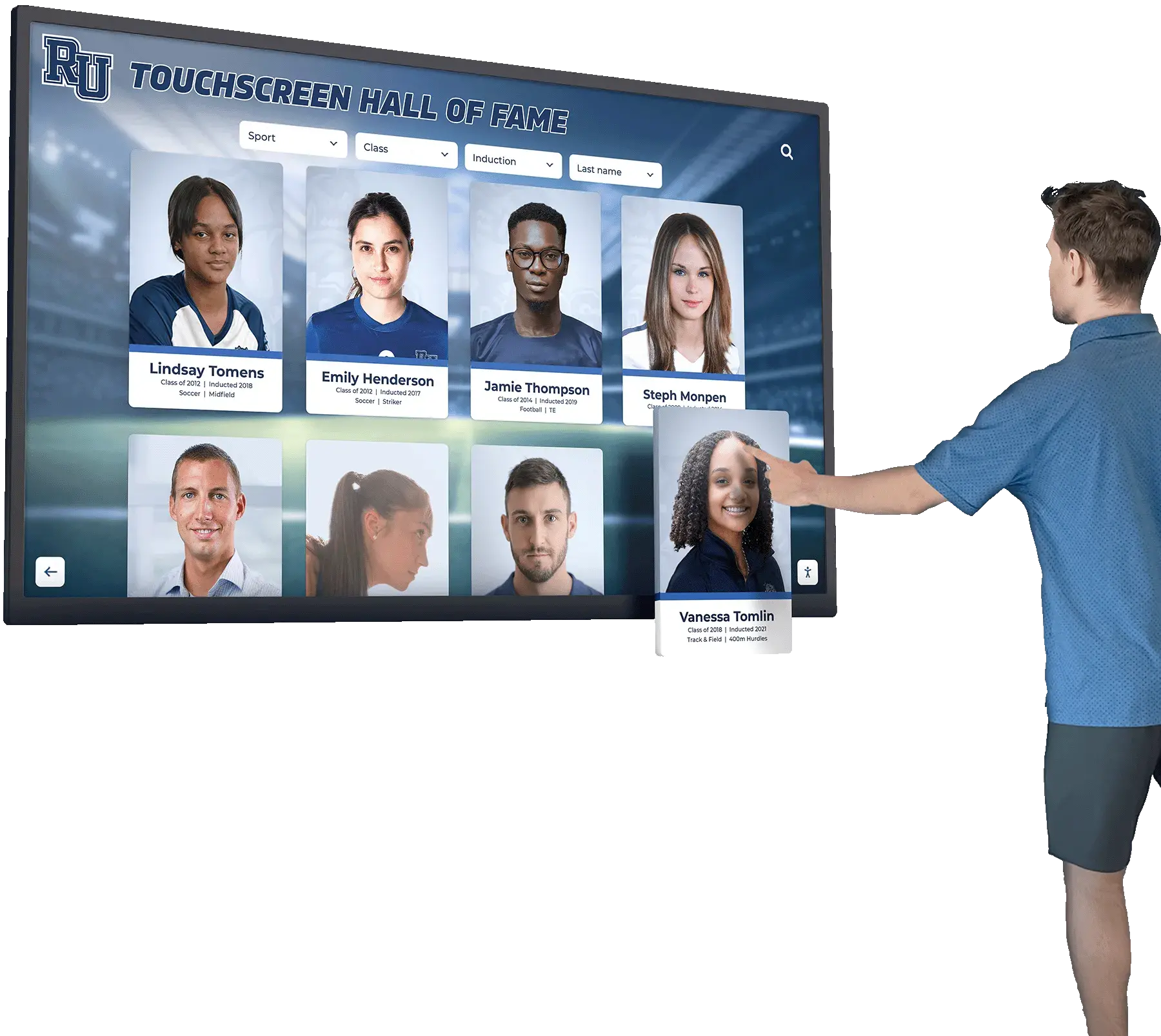
Interactive Touchscreen Installations in Public Spaces
Beyond traditional facilities, forward-thinking programs install interactive touchscreen displays in high-traffic public locations throughout states. State capitol buildings and government offices, major airports and transportation hubs, university campuses and student unions, sports venues and entertainment centers, and libraries and community centers all serve as strategic placement sites for touchscreen recognition displays.
These distributed installations dramatically increase recognition program visibility and engagement. A family waiting at an airport can explore athletic legends from their hometown. Students on campus can discover academic achievers who attended their universities. Sports fans at venues can learn about championship teams and athletes in pre-game entertainment.
Interactive displays allow intuitive touchscreen navigation through content, dynamic content that updates remotely from central management systems, multimedia presentations with videos and photo galleries, customization showing region-specific content based on installation locations, and engagement tracking revealing what content resonates most strongly with visitors.
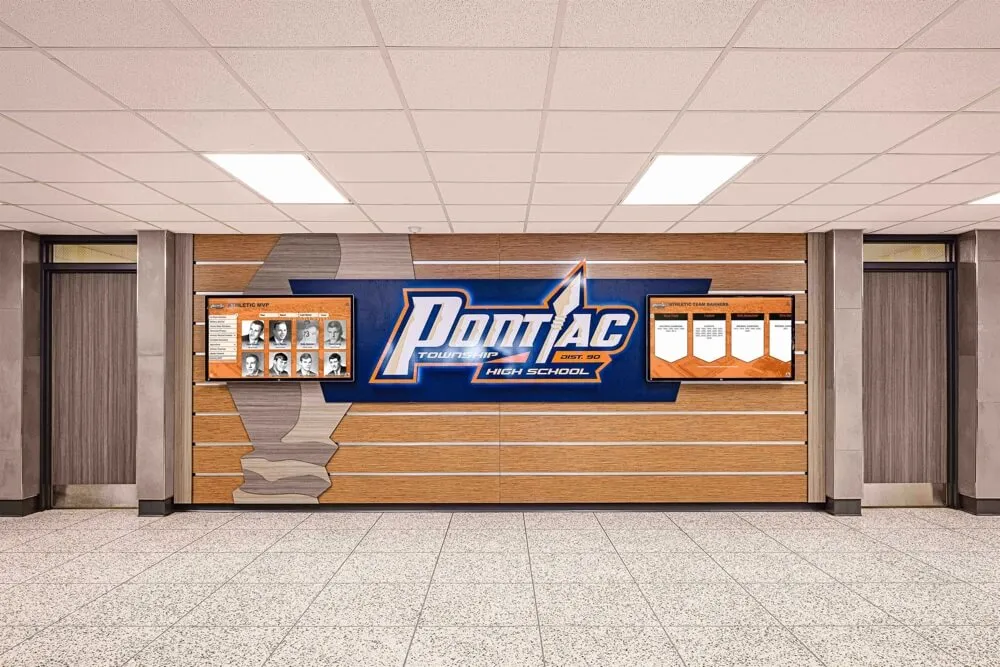

Touchscreen installations in public spaces increase recognition program accessibility
Content Development for Statewide Recognition
Creating compelling content about hundreds or thousands of inductees requires systematic approaches and ongoing commitment.
Research and Documentation Challenges
Statewide programs must document achievements spanning decades or even centuries, often for individuals who lived before modern record-keeping. This historical research requires archiving physical records from newspapers, programs, and documents, conducting oral history interviews with living inductees and associates, digitizing photographs, videos, and artifacts, verifying facts across multiple sources to ensure accuracy, and contextualizing achievements within historical and social conditions.
Many programs partner with state historical societies, university archives, and libraries to access research resources and expertise. Student researchers and volunteers often contribute significantly to documentation efforts, providing labor while gaining valuable experience in historical research and preservation.
The most successful programs establish standardized templates for inductee profiles ensuring consistent information across all individuals. These frameworks typically include biographical basics such as birth date and location, family background, and education, career highlights organized chronologically with key achievements emphasized, awards and recognition received, post-career accomplishments and contributions, personal information about family and interests when appropriate, and legacy statements addressing lasting impact and influence.
Multimedia Content Creation
Modern recognition demands more than text and static photographs. Video content proves particularly powerful for bringing inductees to life through archival footage of athletic performances or artistic work, interviews with inductees about their experiences and perspectives, documentary-style biographical profiles, and testimonials from colleagues, competitors, or those influenced by inductees.
Many halls create different content tiers balancing comprehensive coverage with resource constraints. Essential content covers all inductees with basic profiles including key biographical and achievement information, while enhanced content provides detailed narratives for particularly significant inductees, and premium multimedia packages offer comprehensive video documentaries and extensive galleries for the most prominent figures.
Funding for content development comes from induction fees paid by honorees or nominators, sponsorships from corporations or organizations, grants from foundations and government cultural agencies, fundraising events and donor campaigns, and volunteer contributions of time and expertise.
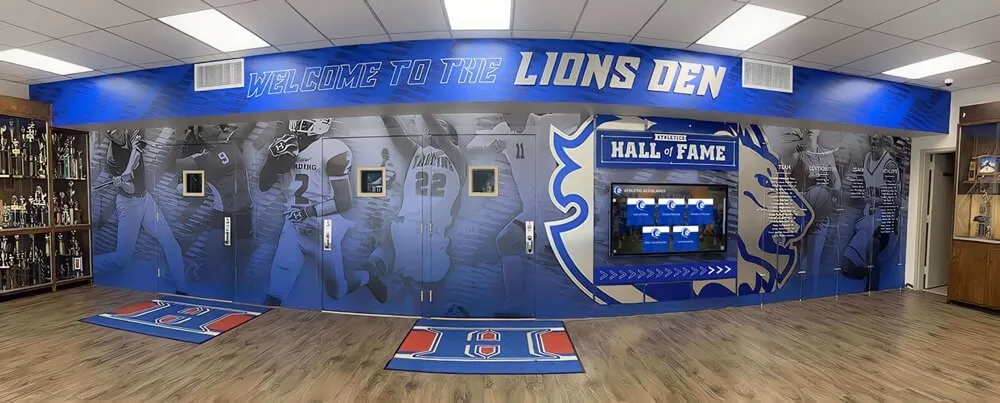

Rich multimedia content brings inductee stories to life for modern audiences
Maintaining Historical Accuracy and Cultural Sensitivity
Statewide programs must navigate sensitive historical issues when documenting achievements from different eras. Individuals who achieved greatness in their fields may have held views or engaged in behaviors that contemporary society finds problematic. Programs must balance honest historical accounting with respectful recognition.
Best practices include providing historical context explaining social norms of different eras without excusing problematic behavior, acknowledging controversies or complexities in straightforward terms, focusing primarily on achievements being recognized rather than unrelated aspects, including diverse perspectives when addressing complex figures, and updating content as new information emerges or social understanding evolves.
Cultural sensitivity also requires ensuring content reflects diverse communities respectfully. This means consulting with communities when developing content about their members, using preferred names and identifiers for individuals and groups, including information about cultural context and significance, presenting achievements through culturally appropriate frameworks, and avoiding stereotypes or tokenization when discussing underrepresented groups.
Funding and Sustainability Models
Statewide halls require substantial ongoing resources to maintain quality operations, recognition standards, and public engagement.
Revenue Sources and Financial Strategies
Diversified funding proves essential for program sustainability. Successful halls typically combine multiple revenue streams including individual membership programs offering benefits like event invitations and publications, corporate sponsorships from businesses supporting recognition missions, induction event revenues from ticket sales and tributes, merchandise sales of branded products and commemorative items, grants from foundations and government cultural agencies, and major gifts from philanthropists supporting capital projects or endowments.
Membership programs create stable recurring revenue while building engaged supporter bases. Typical structures include basic memberships providing newsletters and discounts, supporting memberships with enhanced benefits like special events, leadership circles with exclusive access and recognition, and life memberships requiring larger upfront contributions.
Event revenues depend heavily on successful annual induction ceremonies. These celebrations serve multiple purposes as fundraising galas generating significant income, recognition ceremonies honoring new inductees, community gatherings strengthening supporter connections, and marketing opportunities raising program profiles. Successful events require careful planning around date selection avoiding conflicts with major holidays or competing events, venue choice balancing capacity with atmosphere, program design honoring inductees while entertaining attendees, and sponsorship sales offsetting costs while providing business value.
Operational Cost Management
Major expense categories for statewide halls include physical facility costs when maintaining permanent locations, staff salaries for executive directors and program staff, content development for research and multimedia creation, technology systems and website maintenance, marketing and communications, and event production for inductions and programs.
Programs minimize costs through strategic decisions like volunteer engagement for research, event support, and governance, shared services arrangements with partner organizations, technology solutions providing efficiency and reach at reasonable costs, outsourcing specialized functions rather than maintaining full-time staff, and in-kind donations of services and materials from supporters.
Some halls operate primarily as volunteer organizations with minimal paid staff, while others maintain professional operations with full-time employees. The appropriate model depends on program scale, available volunteer capacity, complexity of operations, and funding availability.

Diversified revenue models ensure long-term program sustainability
Marketing and Public Engagement Strategies
Successful statewide halls maintain high visibility and engagement across geographically dispersed populations.
Building Awareness Across State Populations
Many residents remain unaware of statewide halls even when programs have operated for decades. Building awareness requires consistent multi-channel marketing including media relations generating coverage in newspapers, television, and radio, social media engagement reaching diverse demographics where they consume content, educational partnerships bringing programs into schools, community event participation raising visibility at festivals and gatherings, and influencer engagement with prominent state figures promoting programs.
Annual induction ceremonies provide natural media hooks generating significant publicity. Programs maximize this opportunity through strategic announcements revealing induction classes at optimal times, press conferences with inductees available for interviews, media kits with photos, biographies, and story angles, exclusive content offered to media outlets for advance features, and live event coverage through streaming or broadcast partnerships.
Social media allows ongoing engagement between induction cycles. Successful strategies include daily “on this day” posts highlighting historical achievements, featured inductee spotlights rotating through comprehensive rosters, user-generated content campaigns encouraging supporters to share connections, quiz and trivia content testing knowledge while educating, and behind-the-scenes content showing selection processes and operations.
Engaging Educational Communities
Educational partnerships extend hall of fame missions while building future support. Many programs develop curricula aligned with state standards using inductees as teaching examples, organize field trips or virtual visits for student groups, create student competitions around recognition themes, offer internships providing experiential learning opportunities, and support educator resources making recognition accessible for classroom use.
These educational initiatives serve multiple purposes including inspiring students through achievement examples, building awareness among future supporters, providing educational resources supporting teachers, creating volunteer pipelines through student engagement, and fulfilling broader educational missions beyond simple recognition.
Student engagement often focuses on state history and civics classes, career exploration connecting achievements to professional paths, character education using inductees as role models, writing and research skills through biography projects, and arts education featuring creative achievers as inspiration—similar to approaches discussed in our guide on student achievement recognition.
Leveraging Digital Platforms for Statewide Reach
Digital engagement proves essential for reaching populations across large geographic areas. Comprehensive strategies include website optimization ensuring fast, mobile-friendly experiences, content marketing through blogs, videos, and downloadable resources, email campaigns maintaining regular communication with supporters, online communities providing spaces for fans to connect, and virtual events extending participation to those unable to attend physical gatherings.
Analytics reveal what content resonates most strongly with audiences, informing future development priorities. Programs track website traffic and user behavior, social media engagement and reach, email open and click rates, video view duration and completion, and donation conversions from various channels. This data-driven approach ensures limited marketing resources focus on highest-impact activities.
Digital strategies connect recognition programs with audiences statewide
Technology Solutions for Modern Statewide Halls
Contemporary recognition programs leverage technology to overcome traditional limitations around capacity, accessibility, and engagement.
Comprehensive Digital Recognition Platforms
Purpose-built platforms like Rocket Alumni Solutions provide statewide halls with tools specifically designed for recognition programs. These systems offer unlimited inductee capacity accommodating comprehensive rosters, intuitive content management enabling non-technical staff to update information, powerful search and filtering allowing visitors to discover content, multimedia support for photos, videos, documents, and audio, mobile responsiveness ensuring accessibility across all devices, social sharing integration amplifying recognition reach, and analytics dashboards revealing engagement patterns.
Unlike generic website builders or content management systems, recognition-specific platforms understand unique requirements of halls of fame including inductee profile structures, achievement categorization frameworks, timeline and historical context presentations, advanced search requirements, and ceremonial program integration.
Implementation typically involves initial setup and content migration transferring historical inductee information, design customization matching organizational branding, administrator training ensuring comfortable content management, search optimization helping new audiences discover programs, and ongoing support addressing questions and issues.
Interactive Display Hardware and Software
For public installations, commercial-grade interactive displays create engaging experiences. Key specifications include screen sizes from 55 to 85 inches based on viewing distances and space constraints, touchscreen technology supporting intuitive multi-touch gestures, 4K resolution ensuring crisp text and images, commercial durability rated for continuous operation in public spaces, and content management integration enabling remote updates from central systems.
Software platforms supporting these installations provide touch-optimized interfaces designed for public interaction, dynamic content rotation maintaining visual interest, idle mode attractions drawing attention from passersby, accessibility features supporting diverse abilities, and usage analytics revealing engagement patterns across multiple installation sites.
Distributed touchscreen networks throughout states create coordinated recognition experiences with consistent branding and navigation, centralized content management, location-specific customization, and synchronized updates across all installations—as detailed in our guide on touchscreen software solutions.
Integration with Existing Systems and Databases
Many statewide halls need to integrate recognition platforms with existing organizational systems including membership databases tracking supporters and contact information, donor management systems for development operations, event registration platforms for induction ceremonies, email marketing tools for communications, social media management systems, and analytics platforms measuring overall digital presence.
Well-integrated technology ecosystems reduce administrative burden through automated data flows, eliminate duplicate data entry, ensure consistent information across platforms, enable comprehensive reporting across systems, and create seamless experiences for supporters engaging across multiple touchpoints.
Technical integration typically leverages API connections enabling data synchronization, single sign-on providing unified authentication, embedded widgets displaying content across properties, and automated workflows triggering actions across platforms.
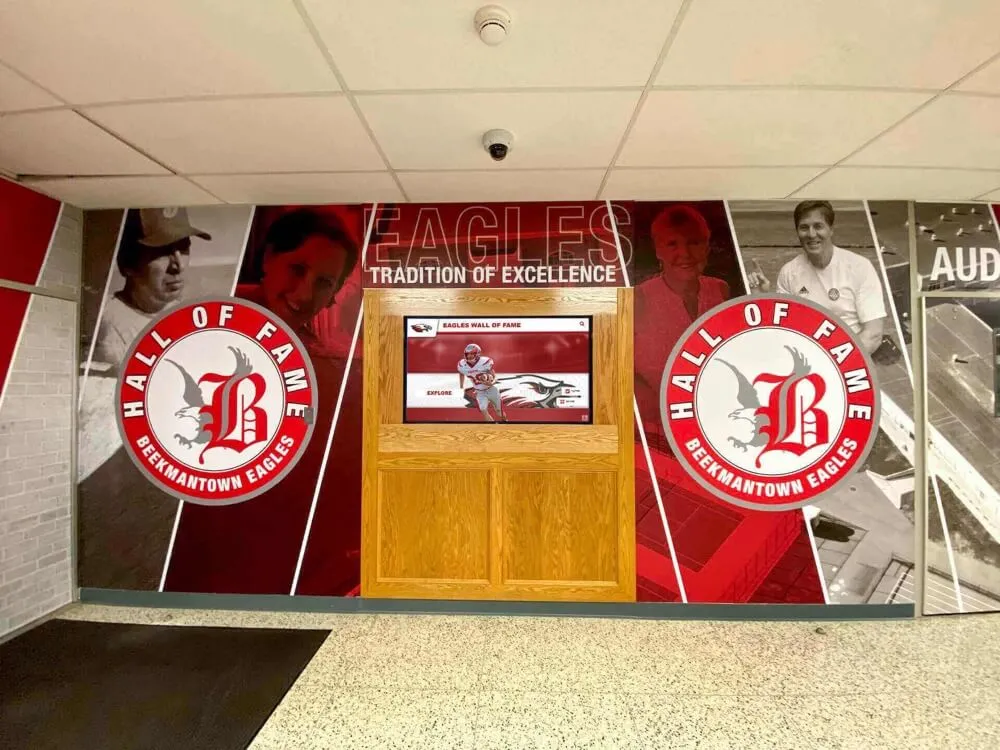

Integrated technology platforms streamline operations and enhance engagement
Case Examples: Successful Statewide Halls of Fame
Examining established programs reveals effective strategies and common challenges.
State Athletic Halls of Fame
Many states maintain comprehensive athletic halls recognizing sports excellence. These programs typically honor athletes from high school, college, and professional levels, coaches and administrators who advanced athletics, significant teams achieving championship success, and contributors supporting athletic development. Some states maintain separate halls for different levels or sports, while others create integrated recognition spanning all athletics.
Selection processes commonly require documented achievement thresholds such as state championships, All-American selections, professional careers, Olympic participation, or significant coaching records. Character considerations ensure honorees represent positive values and role modeling. Geographic representation receives attention to ensure recognition spans entire states rather than concentrating in specific regions.
Successful athletic halls maintain high visibility through partnerships with state athletic associations and high school leagues, collaboration with college athletics departments, connections to professional teams and leagues, and media relationships generating coverage. Annual induction events often align with major sporting occasions like state tournaments, creating built-in audiences and media attention.
Arts and Entertainment Recognition Programs
State arts halls celebrate musicians, visual artists, writers, actors, filmmakers, and other creative achievers whose work brought recognition to states. Selection criteria typically emphasize national or international achievement demonstrating work reached beyond state borders, artistic innovation advancing creative fields or movements, cultural impact influencing communities and future artists, sustained career excellence rather than brief success, and state connections through birth, residence, or subject matter.
Arts halls face challenges balancing popular and critical acclaim, as commercially successful artists may lack critical respect while critically acclaimed creators may have limited public recognition. Selection committees typically include both artistic experts and public representatives ensuring balanced perspectives.
Many arts halls partner with state arts councils and cultural agencies, museums and cultural institutions, arts education organizations, and entertainment industry associations. These partnerships provide research assistance, event venues, promotional channels, and credibility with artistic communities.
Multi-Domain Recognition Programs
Some states maintain halls recognizing achievement across multiple domains rather than focusing on specific fields. These comprehensive programs celebrate athletic excellence, arts and entertainment achievement, business and innovation success, academic and educational contributions, public service and civic leadership, and military service and valor.
Multi-domain halls ensure diverse communities see themselves represented in recognition, prevent any single achievement type from dominating state identity, create opportunities for cross-pollination between different excellence areas, and provide economies of scale in operations and fundraising. However, they face challenges maintaining expertise across all domains, balancing recognition across different fields, and managing selection processes for varied achievement types.
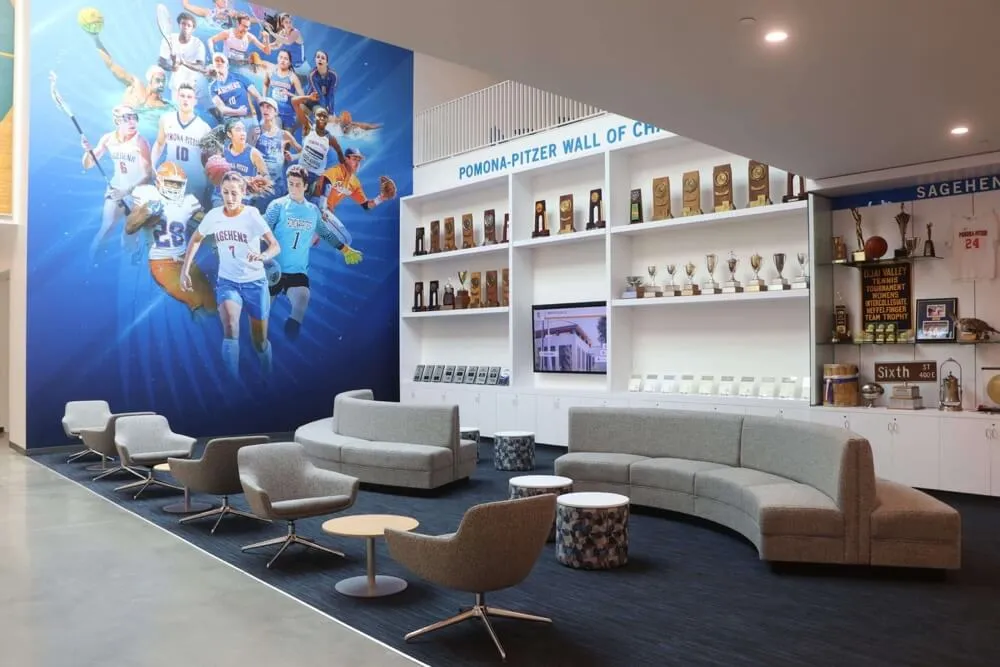

Multi-domain programs celebrate diverse forms of excellence
Addressing Contemporary Challenges and Opportunities
Modern statewide halls navigate evolving expectations and opportunities in recognition practices.
Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion Initiatives
Many established halls confront legacies of underrepresentation affecting women, racial and ethnic minorities, LGBTQ+ individuals, people with disabilities, and rural communities. Addressing these gaps requires proactive initiatives including systematic research identifying qualified candidates from underrepresented groups, outreach to diverse communities and organizations, criteria refinement ensuring varied achievement types receive recognition, historical acknowledgment explaining representation gaps honestly, and representation targets ensuring future balance.
Some programs create special initiatives specifically addressing historical gaps through dedicated induction classes or events focusing on underrepresented groups, research projects documenting previously overlooked achievements, partnerships with organizations serving specific communities, and educational content contextualizing historical inequities.
These efforts must balance correcting historical injustices with maintaining rigorous achievement standards. The goal remains recognizing extraordinary accomplishment while ensuring selection processes don’t systematically exclude entire communities through bias or narrow criteria definitions.
Digital Transformation and Virtual Engagement
Recent years have accelerated digital adoption across recognition programs. Virtual events expanded participation beyond those able to travel, digital content consumption grew dramatically, social media engagement increased, online fundraising became more sophisticated, and virtual reality and immersive experiences emerged as possibilities.
Programs that previously relied primarily on physical locations and in-person events increasingly recognize digital channels as primary engagement platforms for many supporters. This shift requires investment in digital infrastructure, content creation capabilities, virtual event production, social media management, and analytics sophistication.
However, digital transformation creates opportunities for expanding reach beyond geographic limitations, reducing operational costs compared to physical facilities, engaging younger audiences on preferred platforms, providing accessibility for people unable to visit physical locations, and collecting engagement data informing program improvements.
Generational Engagement and Relevance
Statewide halls must engage multiple generations simultaneously including older adults who may prefer traditional engagement methods and content, middle-aged professionals balancing multiple commitments, younger adults consuming primarily digital content on mobile devices, and students and children as future supporters requiring age-appropriate content. Strategies must address these varied preferences through multi-channel approaches, diverse content formats, intergenerational programming, and modernized storytelling while respecting tradition.
Many programs find that involving younger generations in operations—through youth advisory boards, student volunteer programs, social media content creation, and event planning roles—helps ensure relevance while building future leadership pipelines. These emerging leaders bring fresh perspectives on engagement strategies, technology adoption, and cultural relevance while developing ownership in program success.

Successful programs engage multiple generations through varied strategies
Implementation Guide: Launching a Statewide Hall of Fame
For states or organizations considering new recognition programs, systematic planning increases success likelihood.
Initial Planning and Feasibility Assessment
Before launching programs, thoroughly assess whether statewide recognition makes sense and can be sustained. Key considerations include determining if sufficient achievement exists justifying state-level recognition, evaluating whether existing programs already serve similar purposes, assessing potential supporter bases including members and donors, identifying available funding sources and realistic budgets, and understanding competitive landscape and positioning.
Feasibility studies typically involve stakeholder interviews with potential supporters and inductees, market research about public interest and awareness, competitive analysis of similar programs, financial modeling of startup and operational costs, and organizational capacity assessment of human and financial resources available.
This research phase might span six to twelve months of careful investigation before committing significant resources to program launch. Many failed halls resulted from inadequate planning rather than poor concepts or lack of deserving candidates.
Establishing Organizational Structure and Governance
Successful programs require solid organizational foundations including legal entity formation as nonprofit organizations with appropriate tax status, board recruitment bringing diverse expertise and connections, committee establishment for selection, events, fundraising, and communications, staff hiring or engagement when resources allow, and policy development addressing operations, selection, ethics, and finances.
Board composition proves particularly critical for statewide programs. Members should represent geographic diversity from across states, demographic diversity reflecting state populations, professional expertise in relevant fields, networks enabling fundraising and partnerships, and passion for recognition missions. Most effective boards include former inductees, business leaders, media representatives, and community leaders who bring credibility and connections.
Initial boards often include founding members who conceived programs, but must plan succession ensuring ongoing recruitment of engaged, capable leaders. Term limits and structured leadership transitions prevent organizational stagnation while maintaining institutional memory and continuity.
Content Development and Recognition Framework
Before inducting anyone, establish comprehensive frameworks addressing selection criteria with specific standards and thresholds, nomination processes including forms and procedures, evaluation methodology guiding committee deliberations, inductee profile standards ensuring consistent content, recognition materials including plaques or certificates, and ceremony protocols for induction events.
These frameworks should be documented thoroughly, communicated transparently to stakeholders, applied consistently across all candidates, and reviewed periodically for necessary refinements. Clear standards protect program credibility while ensuring fairness in selection processes.
Initial induction classes often include backlog recognition honoring historical figures who would have qualified under established criteria. These founding classes may be larger than annual classes, quickly establishing program rosters while generating visibility through recognizing well-known figures—similar to strategies used in creating alumni halls of fame.
Technology Platform Selection and Implementation
Choose technology solutions supporting program needs and growth plans. Consider whether to invest in purpose-built recognition platforms like Rocket Alumni Solutions or adapt general-purpose content management systems, opt for cloud-based solutions or on-premises installations, prioritize mobile experiences or desktop presentations, emphasize public-facing content or administrative tools, and plan for integration with existing organizational systems.
Platform selection should account for initial implementation costs and setup time, ongoing subscription or license fees, administrator training requirements, content migration from existing sources, customization flexibility matching branding needs, scalability supporting future growth, vendor support quality and responsiveness, and user experience for both visitors and administrators.
Implementation typically requires three to six months for setup, design, content migration, testing, and launch. Many programs conduct soft launches with limited promotion to identify issues before major public announcements.
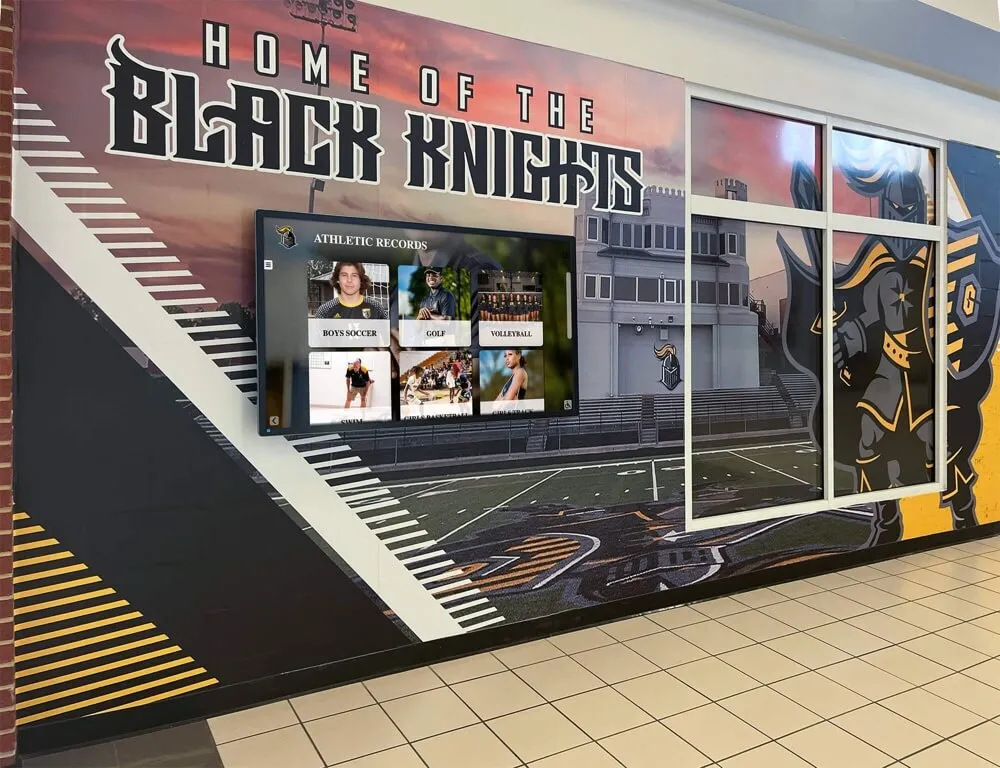

Careful planning and implementation ensure successful program launches
Launch Strategy and Initial Promotion
Program launches require strategic promotion building awareness and momentum including media campaigns announcing programs and inaugural inductions, launch events celebrating first inductees, partnership announcements with supporting organizations, social media initiatives creating online buzz, community outreach in key regions and demographics, and stakeholder engagement with potential supporters and sponsors.
First impressions significantly influence long-term perception, making quality launch execution essential. Programs should ensure complete inductee content is ready, technology platforms function reliably, ceremony planning reflects appropriate dignity, media relationships generate coverage, and supporter cultivation begins immediately building momentum.
Many programs plan eighteen to twenty-four months from concept to public launch, allowing time for thorough planning, organizational development, initial fundraising, content creation, and promotional preparation. Rushing launches without adequate preparation risks undermined credibility that proves difficult to recover.
Conclusion: Preserving State Heritage Through Recognition
Statewide halls of fame serve vital functions in preserving achievements, inspiring excellence, uniting communities, and maintaining connections between past accomplishment and future aspiration. When implemented thoughtfully with rigorous standards, transparent processes, and inclusive representation, these programs become treasured state institutions that strengthen collective identity and pride.
Transform Your Statewide Recognition Program
Discover how modern digital recognition solutions can help your organization honor state-level achievement while engaging audiences across entire states and beyond.
Schedule Your ConsultationThe evolution from limited physical displays to comprehensive digital platforms has transformed what’s possible in statewide recognition. Geographic barriers that once limited engagement have dissolved through online accessibility. Capacity constraints that forced difficult choices about whose achievements deserved acknowledgment have disappeared with unlimited digital storage. Static content that quickly became outdated now updates instantly through cloud-based management.
Modern solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions enable statewide halls to honor every deserving individual comprehensively while creating engaging experiences accessible throughout states and around the world. Interactive touchscreen installations in public spaces extend recognition beyond single facilities, while mobile-responsive websites ensure anyone with internet access can explore state heritage.
The programs that thrive in coming decades will balance tradition with innovation—respecting legacy and established practices while embracing technology and evolving social expectations around representation and accessibility. They will maintain rigorous standards ensuring recognition retains prestige while expanding criteria to acknowledge diverse achievement types and underrepresented communities. And they will engage multiple generations through varied strategies honoring different preferences and consumption patterns.
For states and organizations committed to preserving heritage, inspiring future achievement, and celebrating excellence that transcends individual institutions, statewide halls of fame represent investments that deliver value across multiple dimensions. They document history that might otherwise be lost, create educational resources benefiting schools and communities, strengthen state pride and identity, and inspire current and future residents to pursue their own paths to extraordinary accomplishment.
Ready to explore how digital recognition solutions can enhance your statewide hall of fame program? Learn more about digital hall of fame benefits and discover how modern technology preserves state heritage while creating engaging experiences for current and future generations.

















