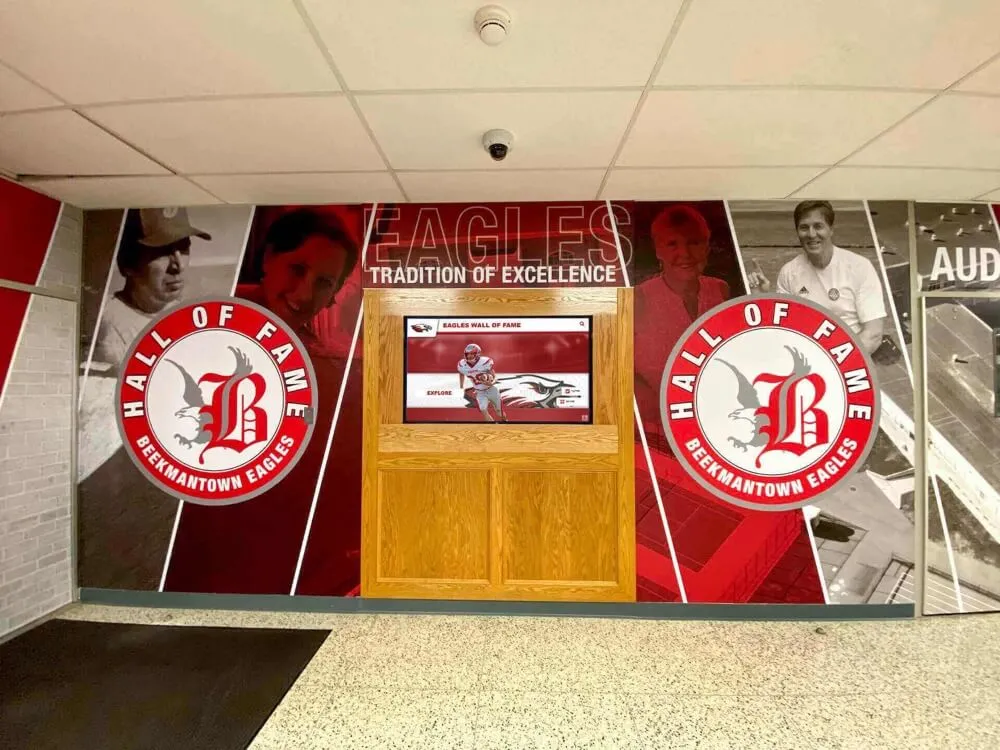
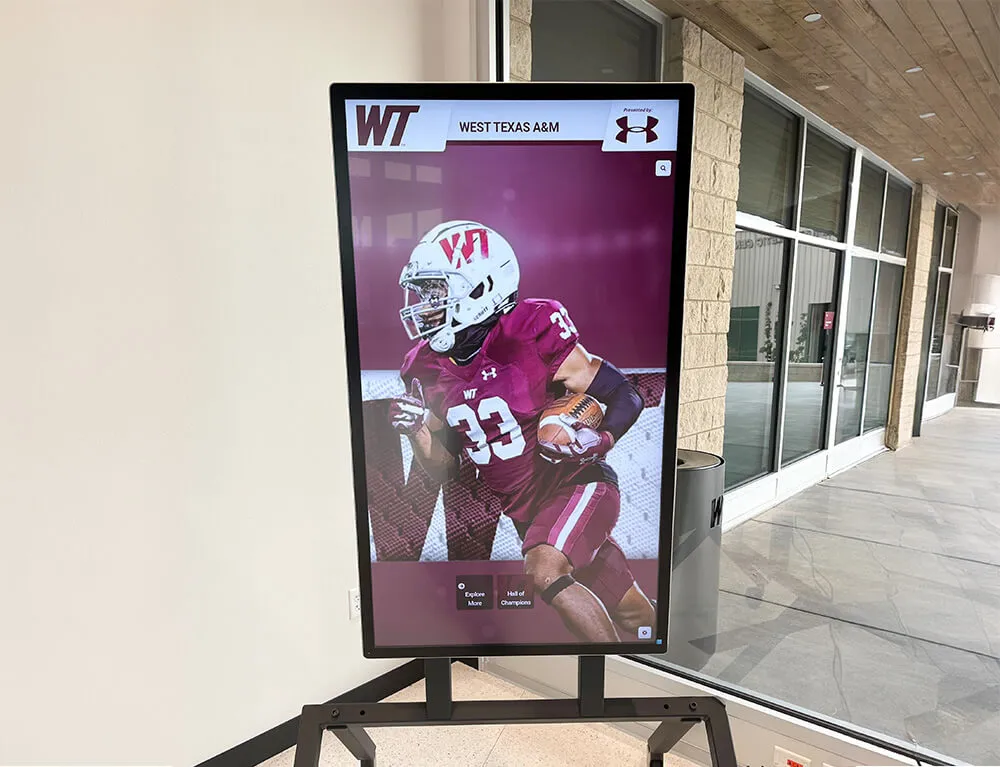
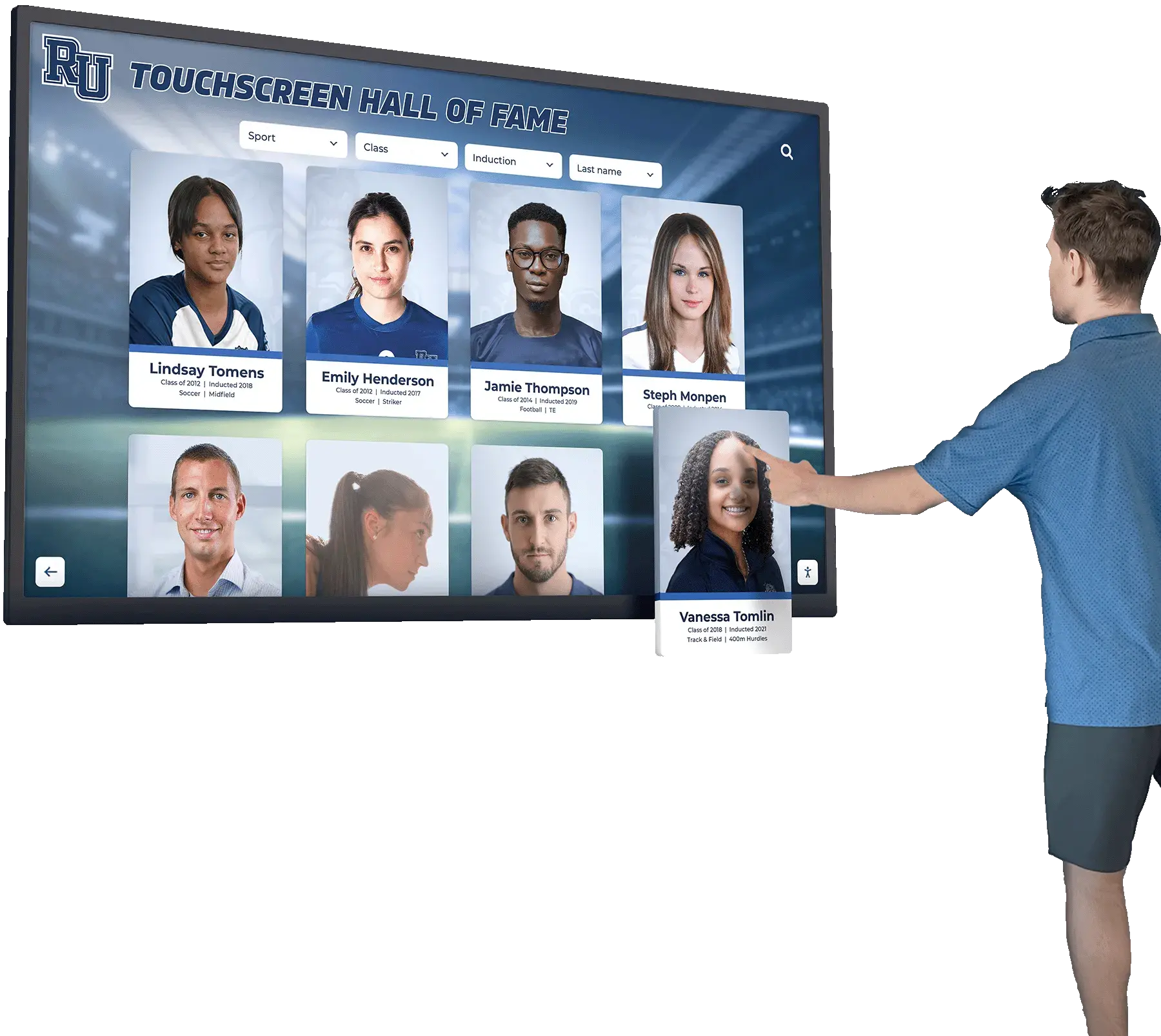
Touchscreen augmented reality displays represent the convergence of physical and digital interaction, creating experiences that fundamentally change how people engage with information in public spaces. By overlaying digital content onto physical environments through interactive touchscreens, AR displays enable visitors to explore content in ways traditional static displays or basic digital screens cannot match.
Educational institutions, museums, corporate facilities, and recognition venues increasingly adopt touchscreen AR technology to deliver experiences that capture attention, facilitate deeper interaction, and make information memorable through hands-on exploration. Where conventional displays present information passively, AR-enabled touchscreens invite active participation, spatial understanding, and personalized discovery that drives measurably higher engagement rates.
This comprehensive guide examines how touchscreen augmented reality displays work, the technology components enabling AR experiences, practical implementation strategies for various facility types, proven applications across educational and recognition contexts, and decision frameworks helping organizations evaluate whether AR-enhanced touchscreens deliver sufficient value to justify premium investments over standard interactive displays.
Organizations implementing recognition displays, interactive wayfinding, or engagement platforms face critical decisions about technology sophistication levels. Understanding where augmented reality capabilities provide significant advantages versus scenarios where standard interactive touchscreens deliver adequate results enables informed investments that match technology sophistication to actual use case requirements and available budgets.

Modern touchscreen AR displays create rich experiences that engage visitors beyond traditional digital signage
Understanding Touchscreen Augmented Reality Display Technology
Before evaluating implementation strategies, establishing clear understanding of what distinguishes augmented reality touchscreens from standard interactive displays prevents confusion about technology capabilities and requirements.
Defining Augmented Reality in Touchscreen Context
Augmented reality overlays digital information onto physical environments, creating composite views that blend real-world contexts with virtual enhancements. In touchscreen applications, AR technology enables users to interact with digital content that appears spatially integrated with physical surroundings rather than displayed as separate interface elements on flat screens.
Key AR Characteristics include spatial registration that anchors digital content to physical locations or objects, real-time interaction enabling users to manipulate AR content through touch gestures, contextual information that appears relevant to user location or focus areas, and spatial presentation creating perception that digital and physical elements coexist in shared space.
Traditional touchscreens display information on two-dimensional surfaces where content exists independently from physical environments. AR touchscreens create three-dimensional interactions where digital content appears to occupy physical space, responds to spatial context, and integrates with real-world elements visible through or around displays.
This spatial integration enables applications impossible with conventional displays: virtual object placement in physical spaces, architectural visualization overlaying digital models onto existing environments, historical recreation showing past conditions in current contexts, and interactive exploration where users manipulate digital representations of physical objects or spaces.
Technology Components Enabling AR Touchscreens
Touchscreen augmented reality displays require several integrated technology components working together to create effective AR experiences:
High-Resolution Displays with sufficient size and clarity enable detailed AR content visualization. Most professional installations use displays ranging from 43 inches to 86 inches with 4K resolution providing visual quality necessary for convincing AR effects where digital content integrates naturally with physical environments.
Precise Touch Sensors detect user interactions with millimeter-level accuracy, enabling manipulation of AR content through intuitive gestures. Capacitive touchscreen technology supporting multi-touch gestures allows users to rotate, scale, position, and interact with virtual objects naturally through familiar smartphone-like interactions.
Powerful Graphics Processing renders complex 3D models, spatial effects, and real-time AR content smoothly without lag that breaks immersion. Dedicated graphics processors handle computational demands of AR rendering while maintaining responsive touch interaction and fluid visual effects.
Spatial Tracking Systems determine display orientation, user position, or environmental context enabling AR content to respond appropriately to physical conditions. Some systems use accelerometers and gyroscopes within display hardware, while more sophisticated installations employ camera-based tracking or external sensors creating comprehensive spatial awareness.
Specialized AR Software Platforms provide development frameworks, content management tools, and rendering engines specifically designed for AR experiences. These platforms handle complex technical requirements of spatial registration, 3D rendering, gesture recognition, and content synchronization that AR applications demand.
Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions integrate these components into comprehensive platforms enabling organizations to implement professional AR touchscreen experiences without requiring internal technical expertise in complex AR development.

Professional AR touchscreen installations require sophisticated hardware and software integration for optimal user experiences
Practical Applications of AR Touchscreen Displays
Understanding where augmented reality capabilities deliver meaningful advantages helps organizations identify appropriate use cases justifying AR implementation over simpler alternatives.
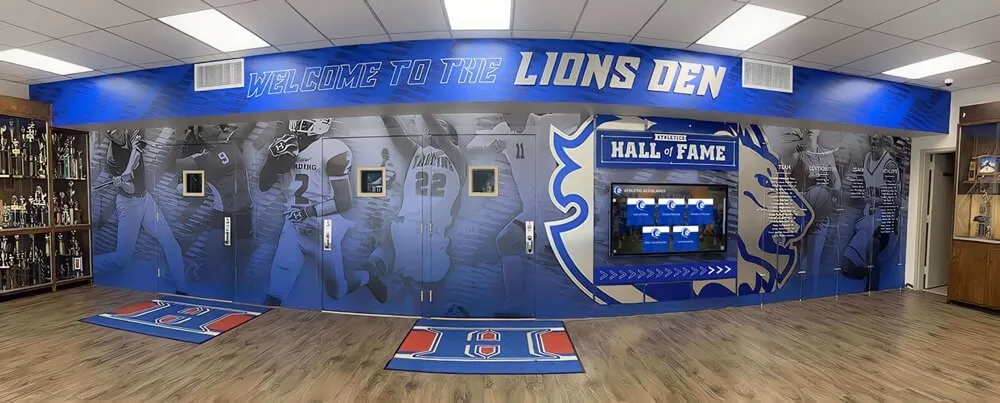
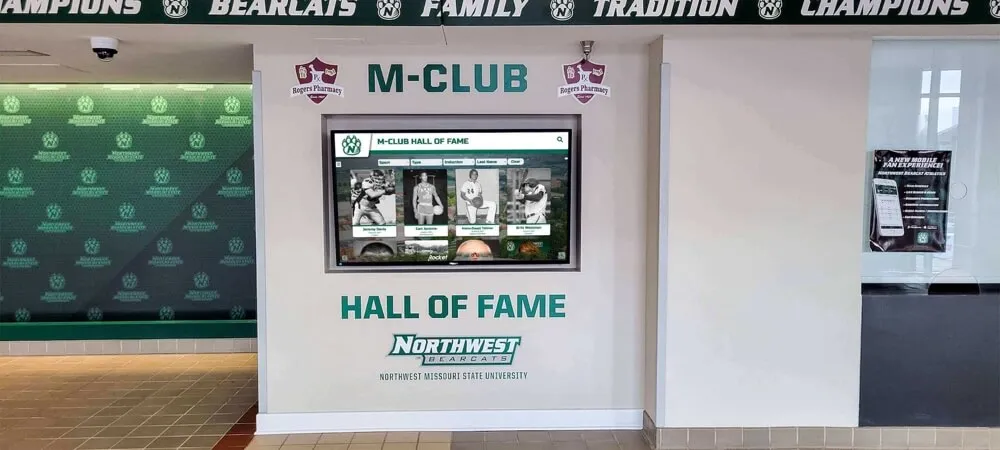
Recognition and Hall of Fame Applications
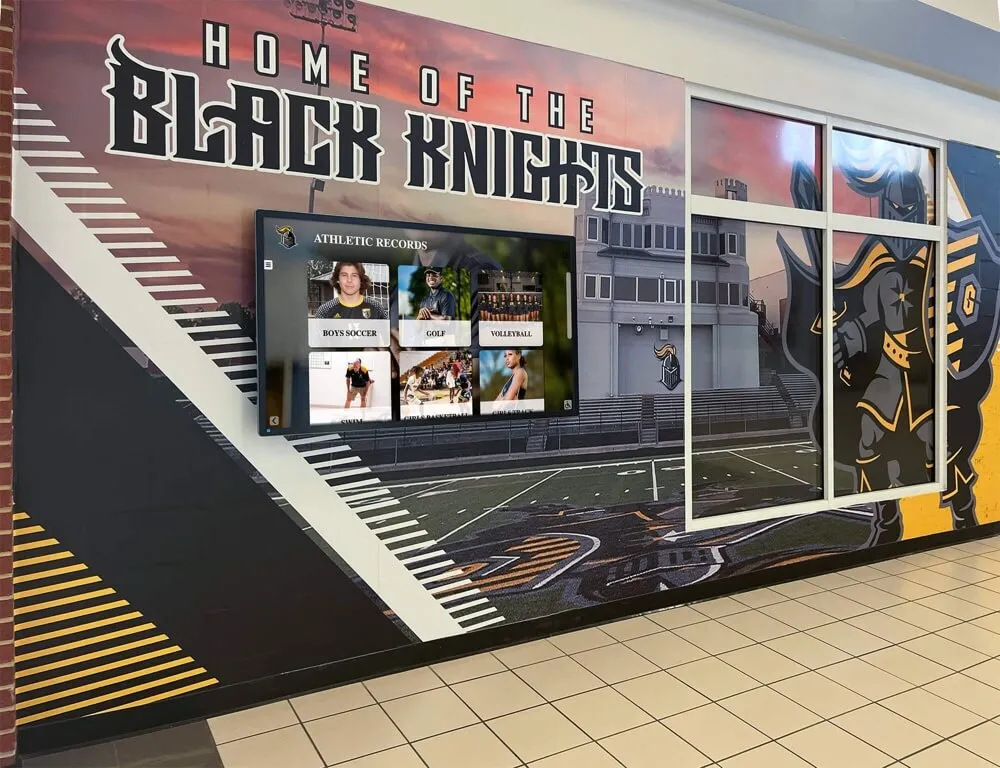
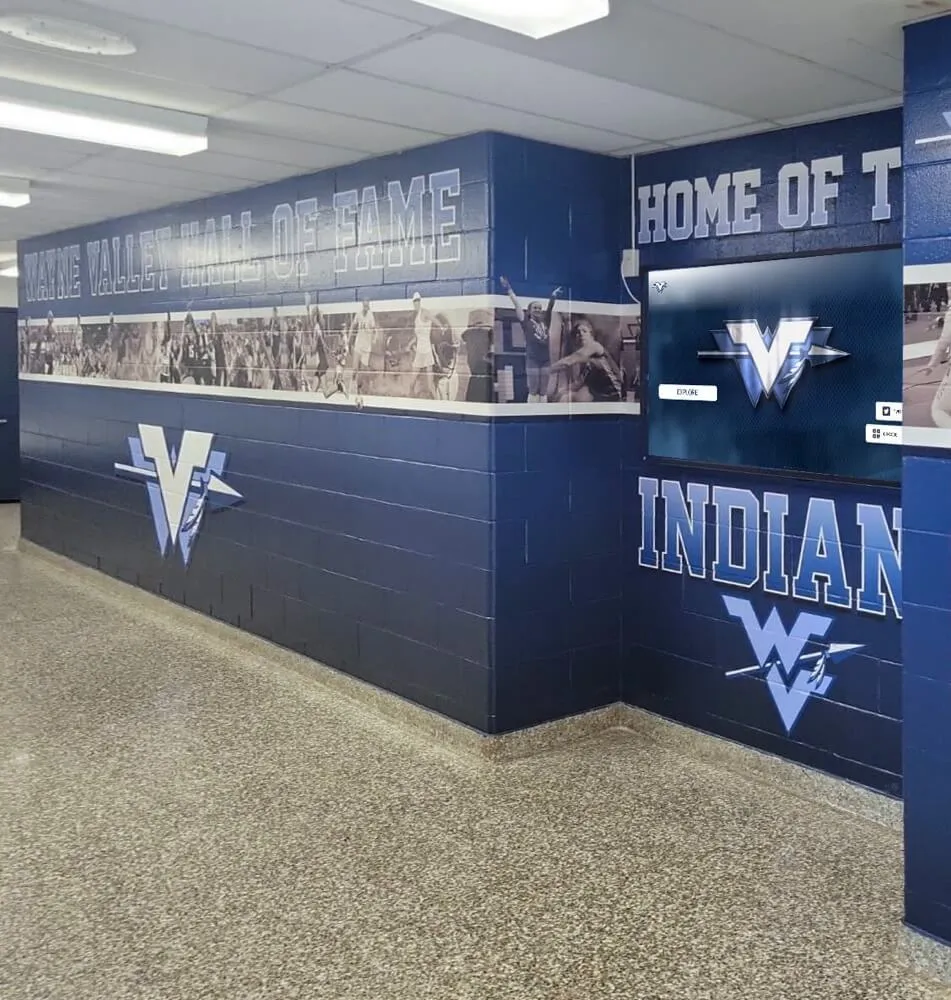
Educational institutions and organizations implementing recognition displays benefit from AR capabilities that bring achievement stories to life through interactive exploration:
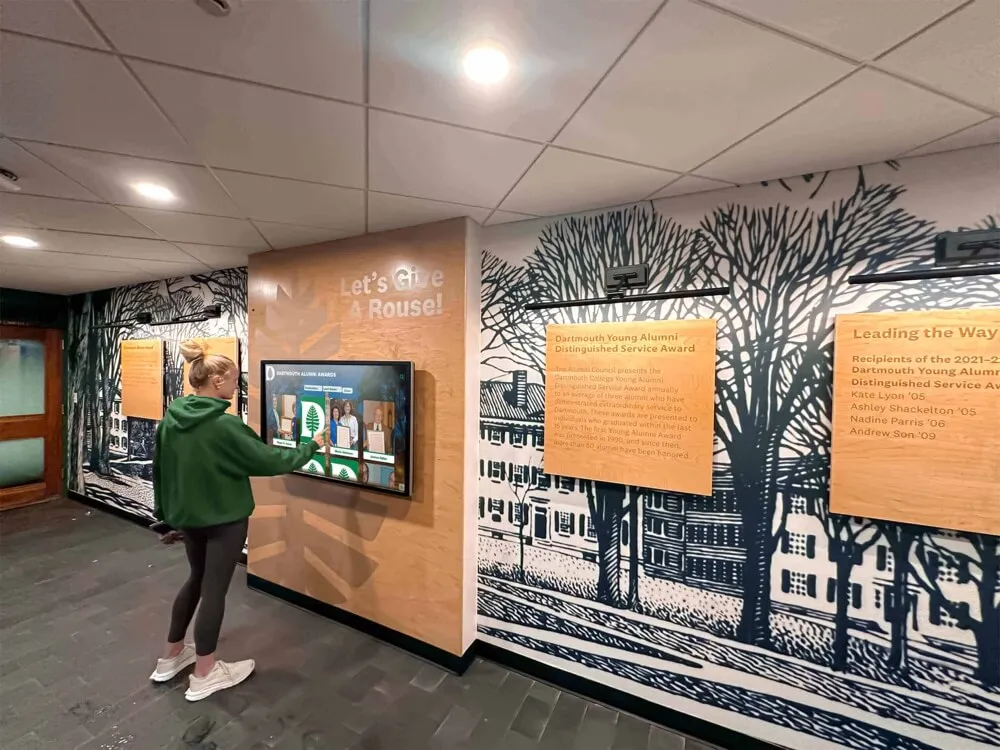
Interactive Biography Exploration allows visitors touching athlete or alumni profiles to reveal expanding content layers—video highlights, career statistics, achievement timelines, and personal stories—that appear spatially integrated with profile photographs rather than replacing them. This depth of content exists within compact interface footprints that don’t overwhelm displays with information density.
3D Trophy and Award Visualization enables virtual examination of physical trophies, medals, or awards from any angle. Users manipulate 3D models through touch gestures, examining details impossible to see when actual trophies sit secured in locked cases. This virtual access democratizes trophy examination while protecting valuable physical artifacts from handling damage.
Timeline Visualization presents achievement histories along spatial timelines where users scroll through decades of accomplishments, zooming into specific years or eras to explore detailed information about achievements during particular periods. The spatial organization helps visitors understand historical context and achievement evolution across program histories.
Comparative Statistics Display overlays performance data, enabling visual comparison of records across different eras, athletes, or achievement categories. AR visualization makes statistical relationships intuitive through graphical representations that respond to user exploration rather than requiring interpretation of static tables or charts.
Organizations implementing digital hall of fame displays increasingly incorporate AR capabilities to differentiate installations and deliver memorable experiences that traditional plaques or basic digital screens cannot match.
Wayfinding and Campus Navigation
Facilities implementing interactive wayfinding systems leverage AR touchscreens to make navigation intuitive through visual guidance that connects digital directions to physical environments:
3D Building Visualization presents architectural models users can rotate, section, and explore to understand facility layouts spatially rather than interpreting two-dimensional floor plans. This three-dimensional orientation helps visitors grasp spatial relationships between floors, buildings, or areas more naturally than abstract maps provide.
Augmented Route Preview shows pathways overlaid onto facility images or video, enabling visitors to see actual corridors, landmarks, and wayfinding cues they’ll encounter while navigating. This preview creates confidence that visitors can follow directions successfully by recognizing visual features along routes.
Interactive Campus Maps enable users to explore institutional grounds through virtual flyovers, zoom into specific buildings or areas for detailed information, and access contextual content about facilities, departments, or services located throughout campuses. The spatial exploration matches how people naturally think about navigation through physical environments.
Accessibility Route Planning visualizes accessible pathways with AR highlighting showing ramps, elevators, automatic doors, and barrier-free routes that visitors requiring accessibility features need to identify. This clear visual distinction helps users plan routes matching their specific mobility requirements before beginning navigation.
Comprehensive guides to touchscreen kiosk software demonstrate how AR capabilities integrate with broader wayfinding platforms serving diverse facility types.

AR-enhanced wayfinding displays help visitors navigate complex facilities through intuitive spatial visualization
Educational and Museum Exhibits
Cultural institutions leverage AR touchscreens to create educational experiences that make learning interactive, memorable, and accessible:
Historical Recreation overlays historical images, architectural renderings, or period photographs onto current environments, enabling visitors to see how locations appeared in different eras. Users can slide between historical and contemporary views, understanding change over time through visual comparison that makes history tangible.
Artifact Examination provides virtual access to detailed 3D models of museum objects, enabling examination from angles impossible with physical displays. Users can zoom into surface details, rotate objects freely, access measurement data, and explore conservation information without risking damage to fragile original artifacts.
Interactive Learning Modules present educational content through touch-responsive AR experiences where users explore concepts through manipulation rather than passive reading. Science concepts, historical events, or cultural information become interactive explorations that accommodate different learning styles and engagement preferences.
Multilayered Information Access uses AR to organize content density without overwhelming interfaces. Surface-level information appears immediately, while users access deeper content layers through deliberate interaction. This progressive disclosure prevents information overload while enabling motivated visitors to explore topics comprehensively.
Resources on interactive displays for recognition show how educational institutions apply AR technology across diverse contexts beyond traditional museum settings.
Corporate and Commercial Environments
Professional settings implement AR touchscreens for purposes ranging from product visualization to employee engagement:
Product Visualization and Configuration enables customers or prospects to explore products through 3D models they manipulate, configure with different options, and examine from all angles. This interactive exploration creates understanding that static images or descriptions cannot deliver, particularly for complex products or customizable offerings.
Corporate History and Culture Display presents organizational stories through interactive timelines, achievement galleries, and value demonstrations that engage employees, visitors, and prospects. AR capabilities make corporate narratives memorable through interactive exploration rather than passive consumption.
Training and Onboarding Experiences use AR touchscreens to deliver interactive learning that new employees or visitors can explore at their own pace. Facility information, process documentation, or organizational knowledge becomes accessible through self-service exploration reducing demands on human trainers.
Data Visualization and Analytics presents complex business information through interactive AR visualizations that users manipulate to understand relationships, trends, or insights. This spatial data presentation often reveals patterns that traditional chart formats obscure, particularly when examining multidimensional datasets.
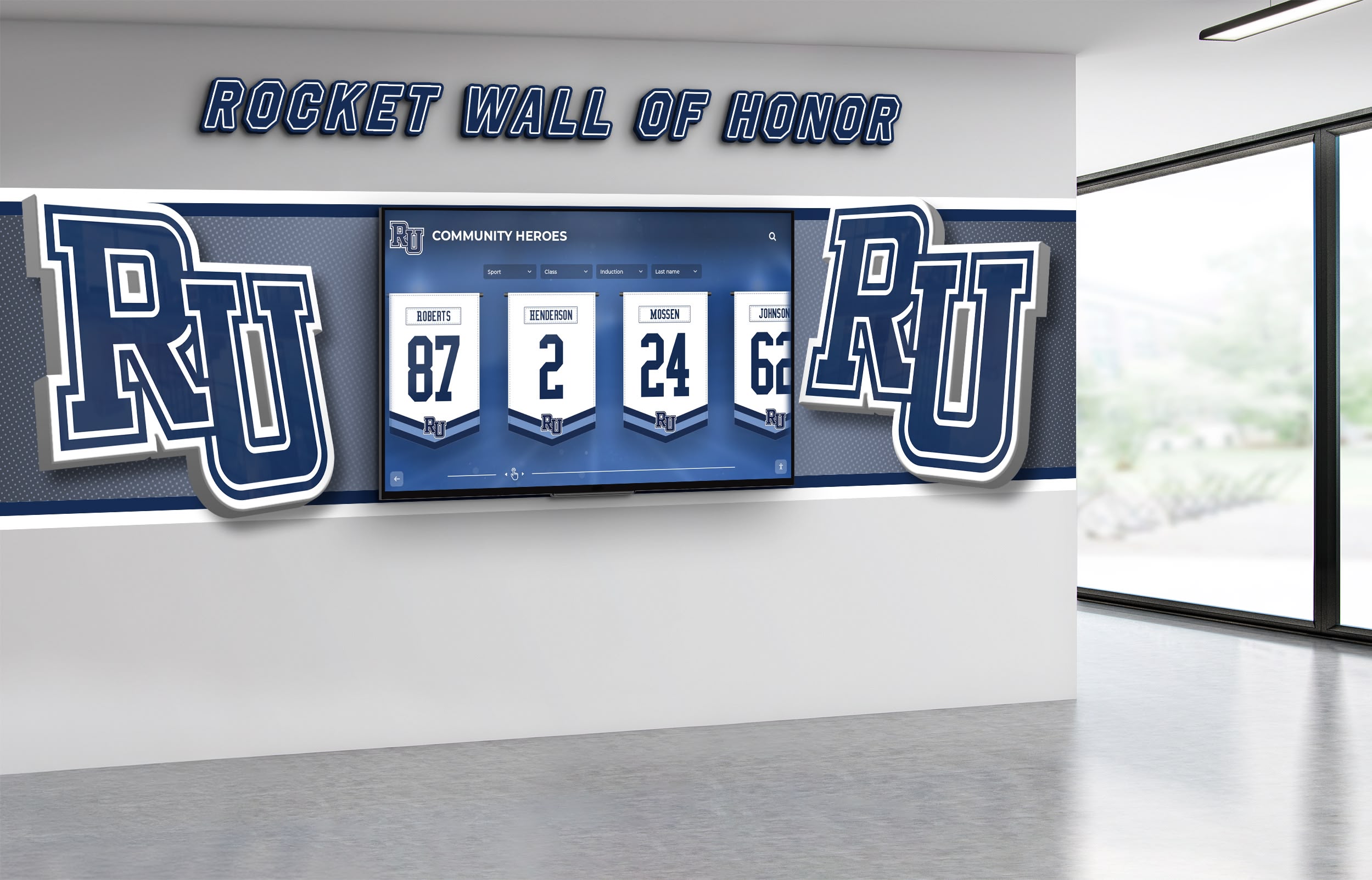

Corporate environments use AR touchscreens for employee recognition, training, and visitor engagement applications
Implementation Strategies and Best Practices
Successful AR touchscreen deployment requires systematic planning addressing technical requirements, content development, user experience design, and operational sustainability.
Content Development for AR Experiences
AR touchscreen effectiveness depends fundamentally on content quality and appropriateness for augmented reality presentation:
3D Model Creation requires specialized skills and tools producing models optimized for real-time rendering on touchscreen hardware. Models must balance visual quality with performance requirements—excessive polygon counts create lag while overly simplified models fail to provide convincing detail. Professional 3D artists understand optimization techniques producing models that render smoothly while maintaining visual quality.
Spatial UI Design differs significantly from conventional interface design. AR experiences must consider how virtual elements integrate with physical contexts, how depth perception affects content readability, and how users interact with content appearing to occupy three-dimensional space rather than flat screens. Specialized AR designers understand these unique considerations.
Progressive Content Disclosure organizes information hierarchies that don’t overwhelm users initially while enabling motivated visitors to access deeper content layers through intentional interaction. Surface content should engage attention and communicate core information within seconds, while detailed explorations reward sustained engagement without requiring it for basic understanding.
Performance Optimization ensures AR content renders smoothly without lag that breaks immersion. This requires testing on actual deployment hardware, optimizing asset file sizes, implementing appropriate level-of-detail strategies, and balancing visual quality against performance requirements. Content that runs smoothly on high-end development workstations may struggle on deployed touchscreen systems if optimization is inadequate.
Organizations without internal AR development capabilities often partner with specialized content development firms or adopt comprehensive recognition platforms providing AR-ready templates and content management systems designed specifically for non-technical administrators.
Hardware Selection and Technical Infrastructure
Appropriate hardware choices enable AR experiences while inappropriate selections create frustrating user experiences regardless of content quality:
Display Size and Resolution must match viewing distances and content detail requirements. Touchscreens viewed from 3-6 feet typically require 55-75 inch displays with 4K resolution providing clarity for detailed AR content examination. Smaller displays or lower resolutions make fine details difficult to distinguish, undermining AR visualization benefits.
Computing Power Specifications need substantial graphics processing capability for smooth AR rendering. Current-generation processors with dedicated graphics cards (not integrated graphics) provide minimum acceptable performance for professional AR installations. Underpowered systems create lag, stuttering, or low frame rates that break visual continuity and frustrate users.
Touch Technology Selection affects interaction quality significantly. Projected capacitive touchscreens supporting multi-touch gestures with low latency provide optimal responsiveness for AR manipulation. Older resistive touch technology requiring pressure or infrared systems with limited gesture support compromise user experience quality.
Environmental Considerations including ambient lighting, physical installation constraints, and climate control affect display visibility and hardware longevity. AR displays perform best in controlled lighting avoiding direct sunlight that washes out screens. Physical mounting must accommodate touchscreen interaction without awkward reach or unstable installations.
Network Infrastructure requirements depend on content architecture. Cloud-based AR systems require dependable high-bandwidth connectivity for content streaming, while locally cached content reduces network dependency but requires substantial local storage. Most professional installations use hybrid approaches balancing performance with update flexibility.
Guides to touchscreen display hardware selection help organizations specify appropriate equipment matching technical requirements to use case demands and budget constraints.

Successful AR touchscreen implementations require careful hardware selection matching performance capabilities to experience requirements
User Experience Design Principles
AR touchscreen effectiveness depends on interface design that makes interaction intuitive rather than confusing:
Immediate Affordance Communication ensures users instantly understand that displays are interactive and how to begin engagement. Obvious touch targets, motion attractors, and clear invitation messages encourage interaction from visitors who might otherwise walk past displays assuming they’re conventional static screens.
Intuitive Gesture Mapping uses familiar interactions that users already understand from smartphone and tablet experience. Pinch-to-zoom, swipe-to-scroll, tap-to-select, and rotate gestures should behave as users expect based on consumer device patterns. Novel gesture requirements create confusion and learning barriers that reduce engagement.
Visual Feedback Confirmation provides immediate responses to user touches, confirming the system recognized inputs and showing what actions resulted. Without clear feedback, users become uncertain whether touches registered or what effect interactions produced, creating frustration that ends engagement.
Graceful Error Recovery enables users to correct mistakes, return to previous states, or start over without feeling trapped by wrong choices. Obvious back buttons, home options, and undo capabilities prevent users from becoming lost within complex content hierarchies or frustrated by dead ends.
Accessibility Compliance ensures AR touchscreens serve visitors regardless of ability. This includes text alternatives for visual content, adjustable interface elements for various heights and reaches, high-contrast modes for users with vision impairments, and alternative input methods beyond touch interaction for visitors with motor control limitations.
Research on designing effective touchscreen experiences demonstrates principles applicable across both standard interactive displays and AR-enhanced installations.
Maintenance and Content Management
Long-term AR touchscreen success requires operational strategies ensuring displays remain functional, content stays current, and systems continue delivering value over multi-year deployment lifespans:
Remote Content Management enables administrators to update AR content, modify displays, or troubleshoot issues without physical access to deployed hardware. Cloud-based management platforms allow content updates across multiple installations simultaneously, reducing operational burden while ensuring consistency.
Scheduled Content Refresh prevents AR displays from becoming stale through regular content updates adding new profiles, rotating featured content, incorporating recent achievements, or refreshing visual presentations. Organizations should establish content update schedules matching institutional rhythms—quarterly for stable content, monthly for dynamic content, or real-time for event-driven displays.
Hardware Monitoring and Maintenance identifies technical issues before they create display failures. Remote monitoring systems track display status, performance metrics, and potential problems enabling proactive intervention. Regular maintenance including screen cleaning, ventilation verification, and component inspection extends hardware longevity.
User Analytics Collection provides insights into engagement patterns, popular content, interaction behaviors, and usage trends informing content improvement decisions. Analytics showing which profiles receive most attention, what content users explore deeply, or where visitors abandon interactions reveal optimization opportunities.
Technical Support Infrastructure ensures problems receive rapid resolution. Organizations should establish clear support contacts, documented troubleshooting procedures, and escalation processes for issues beyond first-line resolution. Reliable support prevents temporary issues from becoming extended outages that train visitors to ignore displays.

Effective content management systems enable administrators to maintain AR displays without technical expertise
Cost Considerations and Investment Justification
Understanding total cost of ownership helps organizations evaluate whether AR touchscreen capabilities justify premium investments compared to simpler interactive alternatives.
Initial Implementation Costs
AR touchscreen deployments require larger upfront investments than basic digital signage or standard interactive displays:
Hardware Costs for professional AR-capable touchscreens typically range from $8,000 to $25,000+ per installation depending on display size, computing power, touch technology quality, and enclosure requirements. This exceeds basic digital signs ($2,000-$5,000) substantially but delivers dramatically different capabilities.
Content Development Expenses vary widely based on AR complexity, 3D modeling requirements, custom interface design, and content quantity. Simple AR implementations with limited content might cost $10,000-$30,000 for initial development, while comprehensive installations with extensive 3D modeling, custom interactions, and substantial content libraries can exceed $50,000-$100,000 for content creation alone.
Installation and Integration including physical mounting, electrical work, network connectivity, and system configuration typically adds $2,000-$8,000 per display depending on facility requirements and installation complexity. Challenging mounting locations or facilities lacking adequate infrastructure increase installation costs.
Platform Licensing or Subscription fees for AR software platforms, content management systems, and ongoing hosting typically range from $200-$2,000+ monthly depending on capability requirements, content volume, number of displays, and support levels. These recurring costs accumulate to substantial investments over multi-year ownership periods.
Operational and Maintenance Expenses
Beyond initial implementation, AR touchscreens require ongoing investment for operational sustainability:
Content Updates and Management represent recurring costs when organizations contract external providers for content creation, 3D modeling, or design services. Internal management using provided CMS tools reduces these costs but requires staff time allocation. Budget $5,000-$20,000+ annually for content refresh depending on update frequency and complexity.
Technical Support and Maintenance ensures displays remain functional. This includes software updates, hardware repairs, troubleshooting, and system optimization. Comprehensive support agreements typically cost $1,500-$5,000+ annually per display, with costs varying based on support responsiveness and coverage comprehensiveness.
Bandwidth and Hosting for cloud-based AR systems require adequate network capacity and remote hosting infrastructure. Monthly costs range from $100-$500+ depending on content delivery requirements, concurrent user loads, and storage needs for 3D models and multimedia assets.
Hardware Replacement and Upgrades become necessary as technology ages or requirements evolve. Organizations should budget for display replacement or major component upgrades every 5-7 years to maintain current capability levels and prevent obsolescence.
Return on Investment Considerations
Despite substantial costs, AR touchscreens deliver value justifying investments for appropriate applications:
Engagement Quality Improvements create memorable experiences that passive displays cannot match. While difficult to quantify directly, enhanced engagement correlates with visitor satisfaction, institutional perception, and mission effectiveness for educational and recognition applications. Organizations report AR displays receiving substantially more interaction than conventional alternatives in comparable locations.
Content Depth Without Physical Expansion enables institutions to showcase extensive information, numerous profiles, or comprehensive histories within compact physical footprints. AR’s layered content architecture delivers information density impossible with physical plaques or static displays, preventing hallway congestion while making more achievements accessible.
Differentiation and Innovation Perception positions organizations as forward-thinking institutions embracing advanced technology for visitor benefit. This perception supports recruitment, fundraising, and reputation objectives particularly valuable for educational institutions and cultural organizations competing for attention and resources.
Long-Term Content Flexibility provides adaptability as institutional priorities evolve. AR platforms enable content updates, presentation changes, and purpose modifications throughout extended ownership periods without requiring physical reconstruction. This flexibility delivers compounding value over time as displays serve evolving needs.
Organizations implementing comprehensive recognition systems like those from Rocket Alumni Solutions benefit from platforms designed specifically for educational recognition contexts with appropriate feature sets, content management tools, and support infrastructure matching institutional requirements.
Investment decisions should balance AR capabilities against practical benefits for specific institutional contexts and use cases
Alternative Approaches: When Standard Interactive Displays Suffice
Understanding where standard interactive touchscreens without AR capabilities provide adequate results prevents unnecessary spending on premium technology that doesn’t deliver proportional value increases.
Use Cases Where AR Adds Limited Value
Several common touchscreen applications see minimal benefit from augmented reality capabilities:
Simple Wayfinding Directories presenting building maps, room directories, or basic navigation typically function perfectly well without AR spatial visualization. Two-dimensional maps with clear search interfaces meet wayfinding needs for most facilities without requiring 3D architectural models or virtual route previews that add complexity without substantial usability improvements.
Text-Heavy Information Kiosks communicating policies, procedures, schedules, or written content don’t benefit from AR capabilities. These applications succeed through clear organization, powerful search, and readable presentation rather than spatial visualization or three-dimensional interaction AR enables.
Basic Recognition Galleries showcasing profiles with photographs, biographical text, and achievement summaries work effectively as standard interactive displays. While AR could enable enhanced interactions, many recognition contexts achieve their objectives through straightforward profile browsing without requiring premium AR development.
Limited-Budget Implementations should prioritize function over technical sophistication when resources constrain investments. Standard interactive touchscreens deliver substantial improvements over static displays at a fraction of AR implementation costs, making them appropriate choices when budgets prevent comprehensive AR development.
Organizations should honestly assess whether AR capabilities meaningfully enhance specific use cases or represent technological sophistication that doesn’t translate to proportional user experience improvements or mission effectiveness gains.
Progressive Implementation Strategies
Organizations unsure about AR value can adopt staged approaches that enable future enhancement:
Start with Standard Interactive Displays implementing comprehensive recognition, wayfinding, or engagement platforms using proven touchscreen technology without AR capabilities. This establishes operational processes, demonstrates value, and creates content libraries that can later incorporate AR enhancements when budgets support expansion.
Design for Future AR Enhancement by selecting platforms, hardware specifications, and content structures that accommodate later AR integration without requiring complete system replacement. Future-ready architectures position organizations to add AR capabilities when circumstances make premium investments feasible.
Pilot AR in Specific Applications testing augmented reality for particular use cases before comprehensive deployment. Limited pilots demonstrate actual engagement improvements and user response in specific institutional contexts, informing broader investment decisions with real-world data rather than theoretical projections.
Phase AR Rollout Across Locations spreading implementation costs across multiple budget cycles while demonstrating value progressively. Initial installations prove concepts and establish operational capabilities before expanding AR displays to additional facility locations.
Guides to interactive display implementation help organizations plan deployment strategies matching resources, priorities, and institutional capabilities appropriately.
Future Trends in AR Touchscreen Technology
Understanding emerging capabilities helps organizations anticipate technology evolution and make implementation decisions positioning them advantageously for future enhancements.
Artificial Intelligence Integration
Machine learning algorithms increasingly enhance AR touchscreen experiences through intelligent automation and personalization:
Content Recommendation Engines analyze user interactions to suggest relevant profiles, topics, or content based on demonstrated interests. These recommendations create more engaging experiences by surfacing content matching individual preferences rather than forcing sequential browsing through extensive libraries.
Natural Language Interfaces enable conversational interaction where users ask questions in plain language rather than navigating structured menus. AI-powered understanding interprets queries like “Show me championship teams from the 1990s” or “Which athletes played both basketball and football” and presents appropriate content responses.
Automated Content Generation uses AI to produce initial drafts of biographical profiles, achievement summaries, or historical narratives from structured data sources. While human review remains essential, AI-assisted content creation reduces manual effort required for comprehensive content development.
Predictive Maintenance Systems analyze display performance data to identify emerging hardware problems before they cause failures, enabling proactive intervention that prevents outages. AI pattern recognition detects anomalies humans might miss, improving operational reliability.
Extended Reality Convergence
Boundaries between augmented reality, virtual reality, and mixed reality applications continue blurring as technologies converge:
Mobile AR Companion Apps extend touchscreen AR experiences to personal devices, enabling visitors to continue exploration on smartphones after leaving physical displays or access AR content throughout facilities via mobile devices rather than fixed installations alone.
Wearable AR Integration allows users with AR glasses or headsets to access content throughout environments rather than at fixed touchscreen locations. While current consumer adoption remains limited, institutional applications may deploy wearable AR for specialized contexts like guided tours or training programs.
Hybrid Physical-Digital Exhibitions combine physical artifacts, printed materials, and AR touchscreen experiences into cohesive presentations where each medium contributes specific strengths. Physical objects provide tangible authenticity while AR delivers contextual information, historical recreation, and interactive depth impossible with physical displays alone.
Resources on digital storytelling platforms demonstrate how institutions create comprehensive narratives across multiple media including AR touchscreens.
Enhanced Accessibility Features
Continued development addresses accessibility limitations making AR touchscreens more inclusive:
Voice-Controlled Navigation enables hands-free AR interaction benefiting users with motor impairments while offering convenient alternatives for any visitor. Spoken commands manipulate AR content, explore profiles, or navigate interfaces without touch requirements.
Haptic Feedback Enhancement provides tactile responses to touch interactions, improving usability for users with visual impairments who benefit from physical confirmation of interface elements and boundaries. Advanced haptic systems create textured sensations communicating different interface elements through touch patterns.
Cognitive Load Optimization through AI-driven interface adaptation that adjusts content density, interaction complexity, and information presentation based on individual user behaviors. Systems detecting user confusion or struggle automatically simplify interfaces or provide additional guidance.
Universal Design Principles increasingly influence AR touchscreen development, creating experiences that work effectively for diverse users regardless of ability rather than requiring special accessibility modes segregating users by disability status.

Future AR touchscreen developments will emphasize accessibility, intelligence, and seamless integration across devices and modalities
Implementation Checklist: Planning Your AR Touchscreen Project
Systematic planning prevents common implementation failures and ensures AR touchscreen deployments deliver intended value:
Requirements Definition
- Define primary use cases and user personas
- Establish success metrics and engagement targets
- Determine content scope and update frequency
- Specify accessibility and compliance requirements
- Identify integration needs with existing systems
Budget Planning
- Calculate total cost including hardware, content, installation, and ongoing operations
- Identify funding sources and approval requirements
- Establish multi-year budget for content updates and maintenance
- Evaluate subscription versus purchase options
- Plan for eventual hardware replacement cycles
Technical Preparation
- Assess facility infrastructure for power, network, mounting
- Specify hardware requirements matching use case demands
- Evaluate platform options and vendor capabilities
- Plan content development approach and resource requirements
- Design installation approach addressing physical constraints
Content Development
- Collect source materials including photographs, biographical information, achievements
- Establish content standards for consistency and quality
- Develop content governance defining ownership and update processes
- Create production timelines aligned with launch targets
- Plan ongoing content refresh strategies
User Experience Design
- Define interaction models and navigation patterns
- Create interface prototypes for stakeholder review
- Conduct usability testing with representative users
- Incorporate accessibility features from project initiation
- Establish visual design aligned with institutional branding
Launch and Operations
- Install hardware and verify technical performance
- Load content and conduct comprehensive testing
- Train staff on content management and basic troubleshooting
- Develop user instructions and promotional materials
- Establish monitoring and support procedures
Organizations benefit from partnering with experienced providers like Rocket Alumni Solutions that guide implementations through proven processes addressing common challenges and accelerating time-to-value.
Conclusion: Matching Technology Sophistication to Institutional Needs
Touchscreen augmented reality displays represent premium technology delivering immersive experiences that substantially exceed conventional display capabilities when applied appropriately to use cases that benefit from spatial visualization, interactive depth, and three-dimensional content exploration. For recognition applications showcasing extensive achievement archives, museums creating educational exhibits, or facilities implementing sophisticated wayfinding requiring spatial understanding, AR capabilities provide value justifying premium investments.
Organizations should honestly assess whether specific use cases meaningfully benefit from augmented reality enhancements or whether standard interactive touchscreens deliver adequate functionality at substantially lower costs. The most successful implementations result from clear-eyed evaluation matching technology sophistication to actual requirements rather than pursuing technical innovation for its own sake.
For institutions ready to implement AR touchscreen experiences, systematic planning addressing content development, hardware specifications, user experience design, and operational sustainability creates foundations for successful deployments delivering lasting value. Organizations should prioritize proven platforms, experienced implementation partners, and comprehensive support infrastructure over lowest-cost options that risk technical problems or inadequate capabilities undermining user experiences.
The touchscreen augmented reality landscape continues evolving rapidly as hardware becomes more capable, software platforms mature, content development tools simplify creation processes, and best practices emerge from early implementations. Organizations implementing AR displays today position themselves as technology leaders while building capabilities and institutional knowledge that enable continuous enhancement as AR technology advances.
Whether implementing comprehensive recognition systems, interactive educational exhibits, or immersive wayfinding platforms, touchscreen augmented reality displays create experiences that engage visitors, communicate information effectively, and demonstrate institutional commitment to innovation that serves stakeholder needs through thoughtful technology application rather than superficial technical sophistication.
Ready to explore how touchscreen augmented reality displays can transform recognition, wayfinding, or engagement in your facility? Book a demo to discover comprehensive platforms designed specifically for educational institutions and organizations seeking sophisticated interactive experiences without requiring internal AR development expertise.